Online presentation links
Program At Glance

Click here to download the pdf version of the program at glance
Detailed Program
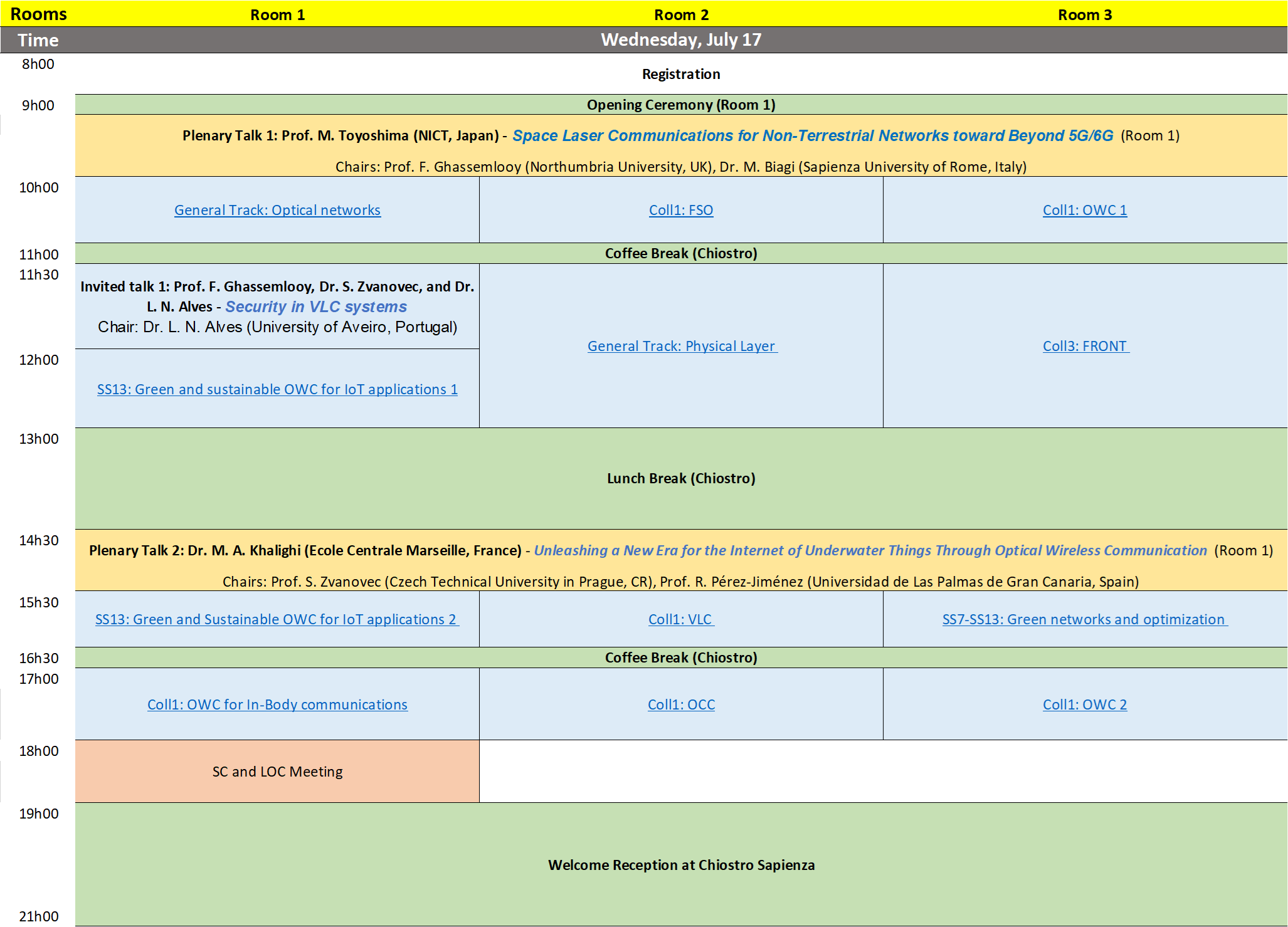
Wednesday 17th July 2024
Chair(s): Prof. Mauro Biagi (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy), Prof. Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University,United Kingdom (Great Britain))
09:00 - Space laser communications for Non-Terrestrial Networks toward Beyond 5G/6G
Prof. M. Toyoshima (NICT, Japan)
In recent years, as discussions on the way how the information and communication technology (ICT) should be in Beyond 5G (B5G) and 6G are accelerating, the space laser communication is becoming more advanced and active in the field of space communications. The realization of the advanced communication network is expected to connect the terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) seamlessly. B5G/6G will require further global spatial expansion of the network than the current 5G, which direction is toward not only two-dimensional so far but also three-dimentional expansion for the mobile platforms called NTN in the future. In this talk, the trend and future vision of the space laser communication technology toward the B5G/6G will be introduced
Chair(s): Dr. Matus Icaza , ULPGS, Spain
10:00 - Quantum OFDM: A Novel Approach to Qubit Error Minimization
Mohammed Almasaoodi and Abdulbasit M. A. Sabaawi (Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME), Hungary); Sándor Imre (Technical University of Budapest, Hungary)
Quantum communication stands on the precipice of a transformative leap with the advent of Quantum Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (Q-OFDM). Drawing from the classical OFDM paradigm, Q-OFDM utilizes the Quantum Fourier Transform (QFT) and its inverse (IQFT)for high-fidelity information encoding and decoding across quantum channels. This study presents a novel Q-OFDM communication model that utilizes quantum superposition and entanglement to distribute data over many orthogonal quantum states, like frequency channels in conventional OFDM. Using the Qiskit platform, we meticulously analyze the Bit Error Rate (BER)across various quantum rotations -Rx, Ry, and Rz- focusing on the rotation angles θ = {20, 50, 100} degrees. Our simulations reveal critical insights into the BER behavior in response to quantum gate operations, with larger qubit counts showing intrinsic error reduction. Accentuating the Q-OFDM system's robustness against quantum noise and operational errors.
10:15 - Fragmentation-Aware Demand Routing on Elastic Optical Network
Der-Rong Din (National ChangHua University of Education, Taiwan)
In this paper, we address the demand routing problem in elastic optical networks (EONs), wherethe objective is to establish suitable lightpaths for each connection request. Our contribution liesin proposing two fragmentation-aware algorithms that take into account both fragmentation andmisalignment factors. These algorithms are designed to determine optimal routing paths,modulation formats, and spectrum assignments in EONs. Through comprehensive simulations, weassess the performance of the proposed algorithms in terms of bandwidth blocking probabilityand demonstrate their efficacy in achieving favorable outcomes.
10:30 - LED Detection and Occlusion Compensation Method for Robust Visible Light Positioning
Wenxuan Pan and Yang Yang (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China);Yao Nie (West Anhui University, China); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, UnitedKingdom (Great Britain))
This paper proposes a light emitting diode (LED) detection and occlusion compensation method(LDOC) for robust visible light positioning (VLP). In the considered system, an image sensorlocates itself by capturing LED images on the ceiling. During this process, lighting conditions andpotential occlusion can greatly affect the robustness of the VLP system. To tackle this issue, wefirst use Gamma correction to accurately obtain the LED contour. Then, the convex hull of thecontour is extracted to restore the ellipse and its parameters. For the striped image formed byrolling shutter effect, we apply the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization algorithm anderode operations to obtain a reliable binarized image, and finally compensate for the stripes anddecode. Simulation results show that LDOC helps existing VLP algorithms achieve centimeteraccuracy even when the contour of LED is 40% occluded to form a randomly shaped concavity.
10:45 - Enabling Anything to Anything Connectivity Within Urban Environments Towards Cognitive Frameworks
Imanol Picallo and Hicham Klaina (Universidad Pública de Navarra, Spain); Peio Lopez Iturri (Universidad Publica de Navarra, Spain); Leyre Azpilicueta and Mikel Celaya-Echarri (Public University of Navarre, Spain); Jose Javier Astrain, Jesus Villadangos and Francisco Falcone (Universidad Publica de Navarra, Spain)
The evolution from Smart Cities towards Cognitive Cities is enabled, among others, by the use offlexible and adaptive communication systems, capable of providing high levels of interactivityamong multiple systems and users. In this work, wireless connectivity in full volumetric scale isanalyzed, in order to provide wireless links between any device/user within the scenario, spanningto different applications from vehicular connectivity at different levels or infrastructure relatedcommunications, among others
Chair(s): Prof. Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
10:00 - Outage Performance of Free-Space Optical Links over Turbulence Channels with Pointing Errors
Rahat Ara (Multimedia University, Malaysia); It Ee Lee (Multimedia University & Northumbria University, Malaysia); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (GreatBritain)); Gwo Chin Chung (Multimedia University, Malaysia)
Free space optical (FSO) communication system presents a viable and innovative technology for enabling point-to-point wireless data transmission across the atmosphere. Atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors impede optical signal propagation in free space, causing the signal to fade at the receiver and degrading connection performance. In order to provide a comprehensive assessment of the partially coherent FSO links, which are used commercially to enhance and support various wireless communication needs, one of the primary performance indicators that has been identified and utilized in the proposed research is the probability of outage. In this paper, we investigate the probability of outage of the FSO system against transmit optical power under clear weather and moderate rain, which is carried out through simulation. Relevant parameters such as link distances, data rates and aperture diameters are considered to optimize the transmitted optical power for maximizing the system performance subject to an outage. It is evident that, shorter link distances and raising aperture diameter in an optimized way can reduce the consumption of transmit optical power while maintaining a desirably low probability of outage.
10:12 - A Method for Generating Random Process Having Given First- and Second-Order Statistics over FSO Channel
Goran T Djordjevic (University of Nis, Serbia); Predrag N. Ivanis (University of Belgrade - School of Electrical Engineering, Serbia); Dejan N Milic (University of Niš & Faculty of Electronic Engineering, Serbia); Jaroslaw Makal (Bialystok University of Technology, Poland); Venceslav Kafedziski (Ss Cyril and Methodius University, Macedonia, the former Yugoslav Republic of)
For the purpose of free-space optics (FSO) channel simulation, we adapt a previously proposed method for generation of stochastic signal samples. By using this method, we generate signal samples that have a given probability density function, as well as a desired autocorrelation function. We use another unrelated method based on stochastic differential equations to generate the stochastic signal samples of the same FSO channel. We compare these two methods based on the resulting probability density functions and autocorrelations. The results are significant for determining important FSO system performance parameters such as error probability, level-crossing rate and average fade duration. The importance of the results is significant specifically in channels where error correction codes are used.
10:24 - Performance Analysis on Real-Time M-QAM Signal Transmission over a Fog-Induced FSO Link
Zun Htay (University College London, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Carlos Guerra-Yánez (Czech Technical University, Czech Republic); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Filipe M. Ferreira (University College London, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
This research conducts a performance analysis on a real-time experimental multi-quadrature amplitude modulation (M-QAM) free-space optical (FSO) system under different fog conditions. The study focuses on experimental investigations to assess the system's tolerance and performance. Experimental results will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the reliability aspects of the M-QAM FSO system, offering practical insights that are vital for real-world applications in challenging atmospheric conditions.
10:36 - Blind Reconciliation with Protograph LDPC Code Extension for FSO-Based Satellite QKD Systems
Cuong Trong Nguyen (The University of Aizu, Japan); Hoang Le (University of Aizu, Japan); Vuong Mai (University of Bradford & Bradford-Renduchintala Centre for Space AI, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Phuc V. Trinh (The University of Tokyo, Japan); Anh T. Pham (The University of Aizu, Japan)
A significant breakthrough in space-based quantum key distribution (QKD) inaugurated by the Micius satellite has brought us one step closer to global quantum networks. An essential step in the post-processing QKD is the key reconciliation (KR), which is to eliminate the mismatch in the raw keys between two legitimate users. However, the fluctuation in the quantum bit-error rate(QBER) caused by the free-space optical (FSO) turbulence channels poses various challenges for the KR design. This paper addresses the design of blind KR schemes for FSO-based low Earthorbit (LEO) satellite QKD systems, which allow operating without a prior QBER estimation. Specifically, we present a novel blind KR scheme with a protograph low-density parity check (LDPC) code extension. The proposed LDPC structure is constructed by gradually extending and exhaustively searching among all possible solutions. The proposed design is evaluated in terms of the final key rate performance over the QKD systems using a dual-threshold/direct detection(DT/DD) scheme. Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of our proposed design compared to the state-of-the-art over different turbulence channel conditions.
10:48 - SDN-Based Mobility Architecture for the FSO Train-Trackside Communication
Nithin Mohan and Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Othman Isam Younus (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Ali Khalighi (Ecole Centrale Méditerranée, France); Thomas Kamalakis (Harokopio University of Athens, Greece)
The key challenge in providing high-speed internet on trains is the rate of handovers due to the speed of the train, which may result in reduced service quality and throughput for under-planned networks. In this manuscript, we propose a software-defined-network (SDN)-based mobility architecture for the handover management in train-trackside communications. An experimental SDN free space optics link using the off-the-shelf components is developed and implemented to evaluate the system performance in terms of the data throughput and the packet loss while handover is performed. We show that the proposed scheme offers seamless handover with the data transfer and throughput of 250 Mbps, respectively dropping down to 196 Mbps during the handover time.
Chair(s): Dr. Xicong Li, Northumbria University, UK
10:00 - Signal Detection in Asynchronous CDMA Communication for Ultraviolet Communication
Yuan Ren and Yueke Yang (University of Science and Technology of China, China); Chen Gong (USTC, China); Zhengyuan Xu (University of Science and Technology of China, China)
Ultraviolet (UV) communication utilizes the atmospheric scattering to achieve non-line-of-sight (NLOS) transmission. This paper proposes two types of detectors, correlation-based detector and multistage detector, for asynchronous code-division multiple access (CDMA) systems. The detector error probabilities are derived theoretically for both correlation-based detector and multistage detector. The detector error probabilities are evaluated via Monte Carlo simulation. The performance improvements of the multistage detector over correlation-based detector are demonstrated.
10:15 - Beacon-Enabled TDMA Ultraviolet Communication Network Design and Realization
Yuchen Pan, Yubo Zhang and Fei Long (University of Science and Technology of China, China); Ping Li, Haotian Shi, Jiazhao Shi and Hanlin Xiao (Xian Modern Control Technology Research Institute, China); Chen Gong (USTC, China); Zhengyuan Xu (University of Science and Technology of China, China)
Non-line of sight (NLOS) ultraviolet (UV) scattering communication can serve as a good candidate for outdoor optical wireless communication (OWC) under non-perfect transmitter-receiver alignment and radio silence. We design and demonstrate a NLOS UV scattering communication network, where a beacon-enabled time-division multiple access (TDMA) multi-node transmission protocol is developed. In our system, light emitting diode (LED) and photomultiplier tube (PMT) are employed for transmitter and receiver devices, respectively. Furthermore, we design protocols for beacon transmission, beacon reception, time compensation, and time slot transition for hardware realization in a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) board based on a master-slave structure, where the master node periodically transmits beacon signals to the slave nodes. We perform field tests for real-time communication network with the transmission range over 110 m ( imes) 90 m, where the network communication system throughput reaches 800 kbps. Experimental results are provided to evaluate the time synchronization error and specify the system key parameters for real-time implementation.
10:30 - Experimental Research on Image Transmission over One Hundred Metres with Limited Bandwidth in a Semantic Ultraviolet Communication System
Xukun Chen, Dahai Han, Min Zhang, Tianzheng Ren and Tongtong Wan (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China)
Currently, ultraviolet (UV) communication is proposed for use in electromagnetic interference environments, while the efficient transmission of images with limited bandwidth has posed a persistent challenge. This paper introduces an LED-based UV communication system combined with semantic compression for image transmission. The experimental results show that the proposed semantic ultraviolet communication (SUC) system could transmit a 7.19 MB image to a file of approximately 304 KB bandwidth with the aid of deep learning. In addition, we calculated the SSIM (structure similarity index measure) and the PSNR (peak signal-to-noise ratio) to assess the robustness of the SUC system. The experimental results demonstrated that the system could work well over 100 metres while sending images with good quality in the face of error bits interference.
10:45 - Experimental Research on Image Transmission with High Compressive Rate in a Semantic Visible Light Communication System
Sihang Liu (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China); Yanzehua Liu (Assessment Center for Energy Saving and Green Development, China); Min Zhang, Dahai Han and Jiaqi Rong (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China)
In this paper, we introduce an image compression technique for semantic communication to optimize the bandwidth constraint in visible light communication (VLC) systems and improve the ease of deployment of the system owing to the high tolerance and fidelity of semantic communication systems. The generalized communication rate was boosted to 400Mbps by transmitting 400Mb sized random images through a physical visible light channel with a single blue LED and the orthogonal frequency division multiplexing format using 16 quadrature amplitude modulation-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing at a communication rate of 50Mbps in an indoor space of 3m. The proposed semantic VLC (S-VLC) system remained stable and exhibited high efficiency at a bit error rate (BER) of 3e-6. Furthermore, the S-VLC systems howed high robustness compared with other systems (JPEG and JPEG2000) at different distances and higher BERs. The structural similarity index measure of the S-VLC system is superior to those of JPEG and JPEG2000.
Chair(s): Prof. Luís Nero Alves (DETI, Universidade of Aveiro, Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal)
11:30 - Security in VLC systems
Prof. Z. Ghassemlooy, Prof. S. Zvanovec, and Prof. L. N. Alves
Chair(s): Dr. Muhammad Ijaz (Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
12:00 - NB-IoT Path Loss Experimental Measurements in Urban Outdoor Environments
Martin Moreno and Daniela Oxman (Universidad de Chile, Chile); Jorge Ignacio Sandoval (University of Chile, Chile); Cesar Azurdia (Universidad de Chile, Chile); Miguel Gutierrez Gaitan (PUC (Chile), Chile & CISTER (Portugal), Portugal); Pablo Palacios Játiva, Dr. (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile); Ali Dehghan Firoozabadi (Universidad Tecnológica Metropolitana, Chile)
This paper presents a performance analysis of the Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) network coverage in urban outdoor environments, focusing on experimental measurements toward path loss modeling. Conducted in a major Latin American city, the study explores the deployment of NB-IoT in LTE guardband 28 (700 MHz), offering valuable information on the network characteristics and coverage performance within this narrow spectrum. Four path loss models are considered, including comparisons between alpha-beta-gamma (ABG) and close-in(CI) empirical models. The end goal is to provide practical tools to optimize the deployment of the NB-IoT network in various urban environments. The results obtained offer a fresh perspective on the importance of experimental validation to accurately predict NB-IoT network coverage and signal quality in a real-world setting. Notably, the work has been carried out in collaboration with a Chilean telecom operator.
12:15 - Emergency Communication Network Based on Drones
Ignacio Marin-Garcia (Escuela Superior Politécnica del Litoral, Ecuador); Patricia Chavez-Burbano (Escuela Superior Politecnica del Litoral, Ecuador); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain); Jose Rabadan (CeTIC-DSC, Universidadde Las Palmas, Spain)
Nowadays, effective communication during emergencies is a critical challenge. Catastrophic events like earthquakes, wildfires, or flooding affect traditional communication networks by damaging the telecommunication infrastructure. One of the consequences of the shrunk working telecommunication infrastructure is that the trapped survivors cannot contact the emergency services or send their locations, resulting in a delayed response from the rescuers. This paper presents the implementation of a temporal Emergency Communication System (ECS) based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), such as drones, for emergencies implemented over the drones working to form an Emergency Communication Network (ECN). This work results reveal effective bilateral connectivity in simulated emergencies; the communication between end users, such as victims and emergency personnel, was viable with less than a 3s delay. Each drone has an average Non-line of Sight (NLOS) communication range of 20 m even when using Commercial off the Shelf (COTS) low-cost hardware, implying that by using dedicated hardware, extensive coverage areas can easily be achieved.
12:30 - Camera-Based Geometric Bilateration for Intelligent Transportation Systems
Othman Isam Younus (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Yingjia Huang (Durham University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Navid Banihasan, Zabih Ghassemlooy and Xicong Li (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (IDeTIC, Las Palmas University of Technology, Spain)
In this paper, for the first time, we propose a camera-based bilateration for intelligent transportation systems. The proposed system is based on the use of visible light communication-based positioning (VLP) and the combination of angle of arrival (AoA) and received signal strength (RSS) methods. We show that our method is capable of retrieving 3D coordinates of the receiver as well as horizontal tilting angles with respect to the transmitter's plane. The proposed algorithm can achieve an accuracy of 20 cm, 2 cm, and 2 mm in estimating the x, z, and y coordinates as well as 0.5º in estimating the tilting angle, regardless of the value of the horizontal tilting angle at a distance of 2 m. We experimentally show that our proposed method outperforms the RSS method in all circumstances and AoA beyond a critical horizontal tilt angle.
12:45 - Modeling of Pedestrian Occlusion Vehicular Visible Light Communication System
Rongrong Yin, Mengfa Zhai, Hao Qin, Kuankuan Jia, Shaoying Ma and Mingqi He (Yanshan University, China)
In this study, we propose a model of the vehicular two-input two-output visible light communication system under pedestrian occlusion. We analyse the number of pedestrians and the position situation. Calculate the probability of pedestrian occlusion to obtain the performance parameters of the communication system, and verify that the effect of pedestrian occlusion on the vehicular visible light communication system is not negligible. Moving vehicles in adjacent lanes create interference but are also potential reflectors. Analyse the effects of different positions of moving vehicles and crossing pedestrians on the V-VLC system. The results show that when the distance between the moving vehicle and the transmitting vehicle is in the vicinity of 0.8 times the longitudinal distance of the communicating vehicle, the bit error rate value decreases to about 50% of that of the communication system without moving vehicles. Moving vehicles affect the performance of the communication system and this effect is positive.
Chair(s): Prof. Beatriz Ortega (ITEAM Research Institute, Spain)
11:30 - Shallow-Water Acoustic Communications in Strong Multipath Propagation Conditions
Iwona Kochanska, Aleksander M. Schmidt and Jan H. Schmidt (Gdansk University of Technology, Poland)
A phenomenon that has a strong impact on signal transmission conditions in Underwater Acoustic Communication (UAC) systems is multipath propagation. As a result of multipath propagation, the transmitted signal undergoes time dispersion, which results in inter-symbol interference observed on the receiving side. Time dispersion is large, especially in horizontal channels in shallow waters, which significantly limits the transmission capabilities of UAC systems operating in these channels. In particularly difficult propagation conditions, such as a very shallow channel, it may be impossible to obtain reliable data transmission without using a matched filtering algorithm in the receiver. The paper presents the results of data transmission tests using two kinds of signals, that require the matched filters in the receiver, namely: DSSS and Multiple LFM. The tests were performed with the use of impulse response of the UAC channel measured during the experiment in a very shallow water in a configuration where the receiving transducer is located at the bottom of the reservoir.
11:52 - Modulation Limitations on Non-Orthogonal Signal Waveform
Yifei Shao, Xiaoyu Shi and Tongyang Xu (Newcastle University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
To save bandwidth, this work compresses orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signals, intentionally breaking their orthogonality to transmit more information in a given time slot, thus achieving higher spectral efficiency. This leads to the creation of spectrally efficient frequency division multiplexing (SEFDM) signals. Due to the violation of the orthogonality, the signal generates inter-carrier interference (ICI), which makes it difficult to recover the original signal at the receiver. This requires a signal detector with a strong anti-interference ability to eliminate ICI, but the traditional signal detection method cannot address this problem well. Therefore, an iterative detector (ID) is used to mitigate the ICI effect and compare with the traditional detection method. The paper conducts a study of signal detection problems with different orders of QAM modulation. Additionally, it examines the influence of changing the number of iterations and compression factors on the performance.
12:15 - Signal Waveform Design for Resilient Integrated Sensing and Communications
Tongyang Xu (Newcastle University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Yujian Ye (Southeast University, China); Christos Masouros (University College London, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
The paper presents an experimental study of data-security in a dual-functional integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system where sensing and communications are carried out using a single hardware platform. The framework is based on orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) in a multi-user multiple input multiple output (MIMO) software-defined radio (SDR) testbed. Over-the-air experiments are conducted to study the robustness of the ISAC in communication security. Results reveal that the ISAC system can generate a directional beam for sensing while the beam also carries communication data. Once an eavesdropper is positioned next to a legitimate user within an appropriate distance, the eavesdropper can capture the signal and recover the data. This alerts that the ISAC transmission has risk in leaking data to eavesdroppers when the eavesdropper is positioned within the ISAC sensing beam range.Therefore, a waveform-defined security (WDS) framework is evaluated here to defend against the potential eavesdropping in ISAC systems illustrating a degradation the eavesdropping performance by 7 dB.
12:37 - Empirical Channel Model of Multiple Lanes Dynamic Vehicle-To-Vehicle Visible Light Communication System
Harpreet Singh Ghatorhe, Seong Ki Yoo and Thomas Statheros (Coventry University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Sujan Rajbhandari (University of Strathclyde, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Farah Mahdi Al-sallami (University of Leeds, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Vehicle-to-vehicle visible light communication (V2V-VLC) channel gain is random due to the irregular shape of the vehicle headlight radiation pattern, dynamic traffic and variation of ambient noise at different times of the day. In this paper, we establish an empirical model of multiple lanes V2V-VLC considering the variation of the received power (in dBm) as an indicator of the channel gain (in dB) on different lanes. We performed experimental received power measurements for a three-lane traffic system in a controlled environment based on realistic vehicle trajectories derived from a traffic dataset. The results show that the statistics of the channel gain do not differ on different lanes and when the vehicle changes lanes. The log-normal distribution closely fits the received power of the V2V-VLC system. The channel gain has a mean value of -78.0dB on the middle lane, which is higher than the mean values on the right and left lanes, which are -78.5dB.
Chair(s): Dr. Dimitris Uzunidis (University of Patras, Greece)
11:30 - AM Based SNR and Bandwidth Estimation for Multi-Level Rydberg Atomic System
Hao Wu and Shanchi Wu (University of Science and Technology of China, China); Chen Gong and Shangbin Li (USTC, China); Rui Ni (Huawei Technologies Co Ltd, China); Jinkang Zhu (University of Science and Technology of China, China)
Rydberg atomic sensors have been seen as a novel radio frequency (RF) measurements and the high sensitivity to a large range of frequencies makes it attractive for communications reception. Based on Lindblad master equation, we discuss the steady state response and bandwidth of four-level Rydberg atomic system under amplitude modulation (AM) signal. Then, we investigate the effect of laser powers and laser detunings on the bandwidth, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and output optical intensity difference. The results provide a guideline to find appropriate operation points for bandwidth and responsiveness optimization.
11:48 - Enhanced XR Services: Performance Analysis with Integration of Passive Optical Networks (PONs)
Akhilesh Patel (IIT KANPUR Uttar Pradesh, India); Rahul Bhattacharyya (IIT Kanpur, India); Yatindra Nath Singh (Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, India)
eXtended Reality (XR) is a potential use case over 5G and beyond 5G technology. For this, in addition to 5G native quality of service (QoS) classes, the access network needs further development to meet the strict performance requirements for XR traffic in terms of reliability,capacity, and latency. In this paper, we investigate the potential of passive optical network (PON) technologies to provide better support for XR services. The considered PON system can provide significantly smaller latency and better bandwidth utilization (BWU), strengthening the overall performance of XR. We have used the XR traffic model as defined by the 3GPP specification. An IPACT-based DBA scheme in a PON system has been simulated to estimate packet delay for the upstream direction for XR traffic. We have analyzed five simulation-based cases to get insight into how the PON system influences the quality of experience (QoE) for XR services. This analysis has allowed us to calculate the number of XR devices supported by the considered method and BWU under a defined delay bound. We have also compared them with the wireless-based XR services' MTP latency.
12:06 - Enhancing Machine Learning Based Physical Layer Performance Estimation of Optical Transmission Links Using Data Augmentation
Amalia Contiero Syropoulou (ASPETE, Greece); Dimitris Uzunidis and Ioannis Tomkos (University of Patras, Greece)
Machine Learning (ML) methods can enhance the accuracy of estimations for the physical layer performance of optical links, especially in cases where the analytical expressions are inaccurate. This accuracy improvement can lead to relaxed operational margins, allowing for an increase in transmission reach and/or enhancement of network capacity. The accuracy of predictions of the ML algorithms strongly depends on the quantity of the training data. For this purpose, we introduce three techniques that can increase the size of the training dataset by several orders of magnitude. We show that using these techniques, the average estimation error can be decreased by 1.5 dB, showing significant gains, especially in small datasets, e.g., of 100 original data. In addition, using the candidate methods, the number of cases with a mismatch higher than 2 dB can also be diminished.
12:24 - Challenges in Scaling Transceiver Bit Rate to 1.6 Tbps and Beyond
Konstantinos Moschopoulos (University of Patras, Greece); Stylianos Sygletos (Aston University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Elias Giacoumidis (VPIphotonics GmbH, Portugal); Ioannis Kontizas (University of Patras, Greece); Andre Richter (VPIphotonics, Germany); Moshe Nazarathy (Technion, Israel Institute of Technology, Israel); Ioannis Tomkos (University of Patras, Greece)
Optical transceivers being the cornerstone of an optical link are required to provide more and more capacity while also meeting more stringent cost and power consumption requirements for next generation optical networks. Optical links were traditionally employed for long-distance communication, it is now increasingly common to utilize optical links for shorter reach applications such as data centers and fronthaul connections, where the required link distances are typically limited to a few kilometers. Unamplified optical links are coming to the forefront of optical communications research with the goal to reduce the cost/power and maximize performance. The optical transmitter, encompass both electronic and photonic subsystems. The elimination of optical amplifiers in the optical link dictates to investigate different aspects of the transmitter that for decades where not properly addressed, like the optimal use of Mach Zehnder modulators (MZM) or the challenges from the limitations of the bandwidth of electronics. In this paper we discuss the limitations of the conventional transmitter approaches, and we study the tolerances of a new type of transmitter that we have introduced recently that incorporates an optical digital-to-analog (DAC) converter which promises to achieve terabit per second scalability by utilizing low-order electronic DACs.
12:42 - Online Kernel-Based Phase Recovery for Parametrically Amplified Optical Transmission
Long Hoang Nguyen, Sonia Boscolo and Stylianos Sygletos (Aston University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
We present a kernel adaptive filtering-based phase compensation method for transmission links with multiple cascaded fibre-optical parametric amplifiers (FOPAs). Our proposed algorithm predicts and cancels the phase distortions induced by pump-phase modulation and laser line-width across all amplification stages. Through numerical simulations, we show effective correction of phase errors in 16-quadrature-amplitude modulation signal transmission, substantially surpassing the performance of conventional carrier phase recovery.
Chair(s): Prof. Mohammad Ali Khalighi (Ecole Centrale Méditerranée, France), Prof. Anna Maria Vegni (Roma TRE University, Italy)
14:30 - Unleashing a New Era for the Internet of Underwater Things Through Optical Wireless Communications
Dr. Ali Khalighi (Ecole Centrale Marseille, France)
The recent proliferation of human activities in underwater environments, spanning environmental monitoring, underwater exploration, offshore oil field exploration/monitoring, disaster prevention, etc., has increased the need for reliable and secure underwater communications. In particular, as robotics play an ever-growing role in underwater missions and with recent advances in the design and development of autonomous underwater vehicles, there is a growing demand for broadband underwater links with significantly enhanced performance. In the context of the Internet of Underwater Things paradigm, underwater wireless optical communication emerges as a promising technology capable of providing very high data rates, low delay latencies, low energy consumption, and minimal environmental impact. This presentation provides an overview of the latest advancements in the UWOC links, with a specific emphasis on techniques aimed at enhancing link robustness, range, and data rate
Chair(s): Prof. Wasiu Popoola, Edinburgh University, UK
15:30 - Enhanced Responsivity and Detectivity for Perovskite Based Self-Powered Photodetector for Low Power VLC Applications
Nadia Anwar, Iqra Anjum, Muhammad Usman and Usman Habib (Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, Pakistan); Muhammad Usman Hadi (Ulster University & Nokia Bell Labs, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Muhammad Ijaz (Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Perovskite based self-powered photodetectors can be used for future VLC networks employing low-power transmitters and large number of photodetectors to make use of the modern receiver diversity techniques. This paper presents a methylammonium lead bromide (MAPbBr3) based photodetector which can provide high responsivity and detectivity. Composition engineering is performed by using a TiS3 electron transport layer (ETL) and numerically evaluating the performance by varying the absorber layer thickness. Simulation results show an improved performance as compared to the recently reported designs, with responsivity of 0.625A/W and detectivity of 1.7e13 Jones at 800nm wavelength for 1µm perovskite absorber layer. Thus the proposed perovskite based photodetector can be used for modern energy efficient VLC applications.
15:45 - Self-Powered IoT Node Utilizing a Perovskite Photovoltaic for Green OWC Systems
Carlos Iván del Valle Morales (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid & Optiva Media, Spain); Othman Isam Younus (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Juan Carlos Torres Zafra (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Jose M. Sánchez-Pena (Carlos III University of Madrid, Spain); Iñaki Martinez-Sarriegui (TECNALIA, Spain)
In this work, we investigate the viability of integrating Perovskite Photovoltaic (PPV) cells into Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices for data receiving and energy harvesting simultaneously to have a dual self-powered IoT node. The results show a bandwidth of ~1KHz for data receiving. The optical link is based on VLC and achieves a maximum range of 1.75m. The energy harvesting module is based on a PPV array of 4,000mm2, which improves the autonomy of the IoT node by more than 20% in an indoor environment, and the IoT node's autonomy is enhanced by more than 34% in an outdoor environment.
16:00 - Experimental Proof-Of-Concept Design of Self-Power LiFi Communication System for IoT Applications
Filip Vladuceanu (Manchester Metropolitan University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Muhammad Ijaz (Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Sunday Cookey Ekpo (Manchester Metropolitan University & Akwa Ibom State University of Technology, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Bamidele Adebisi (Manchester Metropolitan University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile); Pablo Palacios Játiva, Dr. (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile); Salman Ghafoor (National University of Sciences and Technology, Pakistan)
This paper investigates the performance of a proof-of-concept self-power Li-Fi System Prototype for future Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The proposed experimental setup is capable to provide low bandwidth connectivity and wireless energy harvesting simultaneously and consist of multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) LiFi transceiver. Different configurations of MIMO LiFi receiver are used in series and parallel combinations and tested experimentally to evaluate bandwidth and power harvesting. Experimental results show that the series combination of solar cells in 4x4 achieved higher bandwidth, B=71KHz due to better accumulation of signal to noise ratio (SNR). The larger configurations in 4x4 series achieves the higher electrical power harvested of 80mW than 65mW in parallel combination. This harvested power could be stepped up and stored. Furthermore, for the communication performance, an on-off keying (OOK)- non return to zero (NRZ) modulation is implemented and tested. The results show that using a SISO system a data rate of 50Kb/s is achieved at BER= 5x10^-3, however, the data rate is doubled to 100Kb/s at BER= 2.810^-3 using a 4x4 MIMO configuration in series due to higher SNR and improved bandwidth. The results could be further justified with the received signal eye-diagrams and histograms.
16:15 - Enhancing Green Underground VLC Channels with Polar Codes and Multiresolution Analysis
Jonathan Pereira-Mendoza (Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile); Pablo Adasme (University of Santiago de Chile, Chile); Gustavo Gatica (Universidad Andres Bello & Santiago de Chile, Chile); Pablo Palacios Játiva, Dr. (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile); Cesar Azurdia (Universidad de Chile, Chile); David Zabala-Blanco (Universidad Católica del Maule, Chile); Muhammad Ijaz (Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
The core objective of this study is to leverage channel coding through Polar Codes and Multiresolution Analysis (MRA) to enhance the efficiency of Visible Light Communication (VLC)channels and aid in eliminating carbon emissions from underground communications. To implement the Polar Codes, an (N=K/2) configuration of frozen bits is utilized. Additionally, the Daubechies Wavelet family, featuring 5 levels of decomposition, is incorporated within the MRAfilters. The effectiveness of each method is evaluated independently, without integrating any supplementary techniques into the communication channel. The findings demonstrate a notable improvement of 8 dB in channel performance when both methodologies are synergistically applied.
Chair(s): Dr. Milica Petkovic (Faculty of Technical Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Serbia)
15:30 - Experimental Demonstration of Text and Audio Transmission over Single Channel and Relay Assisted VLC Systems
Champalal Lalani, Harsh Meena, Lovish Goyal, Aashish Mathur and Nitin Bhatia (Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, India)
There is an increasing need for high data rate and massive connectivity requirements in the Internet of Things (IoT) based communication applications. Therefore, visible light communications (VLC) have become a popular area of research for both academia and industry. This is due to wide bandwidth, license-free spectrum, energy efficiency, and low implementation cost of VLC. In addition, traditional radio frequency (RF) based communications face issues with spectral congestion. In this paper, we develop an experimental setup of VLC based data transmission and reception. We demonstrate text and audio transmission over a single VLC link of upto 2 m using light emitting diode (LED) and collimating lens as the transmitter and receiving lens with a PIN photodetector as receiver. VLC system's link length improved up to 4m with an amplify-and-forward (AF) relay for data transmission and reception. Further, it is presented that with 4 LEDs, the distance for error-free transmission for text data increased from 50 cm to 180cm. Useful insights into the VLC systems performance are obtained through the experimental measurements of the received power for various link lengths, receiver angular position with respect to the transmitter, and the number of the transmitting white LEDs used.
15:45 - LiDrive: A LiFi Solution Compliant with ITU-T G.hn Standards for Commercial Deployment
Xicong Li, Hoa Le Minh, Zabih Ghassemlooy and Richard Binns (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Ambrose Eromosele (Integrated System Technologies, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Geoffrey Archenhold (Integrated System Technologies Ltd., United Kingdom (Great Britain))
This paper introduces a commercial LiFi system, LiDrive®, developed jointly with Integrated System Technologies (IST) and the Optical Communications Research Group at Northumbria University, UK. The paper introduces the system architecture followed by the performance of the system in terms of net throughput. A tech-economical perspective is provided with outlooks for the future LiFi technology evolution and commercialisation.
16:00 - IRS-Aided Handover Technique in Indoor VLC Blockage-Affected Systems
Anna Maria Vegni (Roma TRE University, Italy); Alessandro Romano (Roma Tre University, Italy); Himal A Suraweera (University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka)
Handover management in indoor visible light communication systems can be enhanced by the use of intelligent reflective surfaces (IRS). In general, the use of IRSs avoids block-age conditions, since they allow to exploit non-direct connectivity links, guaranteeing a seamless connectivity to the end user. On the other hand, in realistic scenarios, blockages due to shadowing and obstacles may occur, affecting the condition of line-of-sight from a light emitting diode (LED) to a receiver. Therefore, it is relevant to provide solutions for redirecting the optical signal from the blocked LED to the end user. In this paper, we present an IRS-aided handover technique that initiates a hard or soft handover triggered by the blockage probability affecting the LED luminaries. The proposed approach has been assessed in terms of achievable data rate and number of handovers, for different user speed and random mobility patterns, as well as number of LEDs deployed in a given indoor scenario. Simulation results reveal the benefit of using IRSs in avoiding connectivity holes, as proactively initiating a hard/soft handover toward a neighboring LED access point or an IRS, based on any blockages affecting direct and no line-of-sight links. Comparing the performance achieved without IRS and for multiple IRSs, we show that the effect of multiple IRSs is affected by geometrical parameters of the LED luminaries.
16:15 - VLC/RF Network Simulator: An Integrated Approach to Optical and Radio Frequency Connectivity
Lisandra Bravo (University of Concepción, Chile); Danilo Bórquez-Paredes (Universidad Adolfo Ibañez, Chile); Samuel Montejo (Universidad Tecnologica Metropolitana, Chile); Lien Rodríguez López (San Sebastian University, Chile); Gabriel Saavedra (Universidad de Concepción, Chile)
Hybrid systems composed of visible light communication (VLC) and radio frequency (RF) networks have gained great popularity in recent years, due to their great adaptability, flexibility and reliability in different scenarios. To ensure the success and efficiency of a hybrid VLC/RF network, it is essential to have a simulator that allows different aspects to be evaluated and configured. Using a simulator, it is possible to simulate different scenarios and analyze the network response to these changes, identifying potential problems and defining improvement strategies. This work proposes the development of a discrete event simulator for a hybrid VLC/RF network in an indoor hybrid environment composed of VLC and RF networks. The results obtained with the simulator allowed to evaluate and analyze the performance of the hybrid VLC/RF network in terms of number of users per access point, connection time, slot and frame allocation for connection and delay. It was demonstrated that the hybrid VLC/RF network was able to satisfy the connection needs of all users with different connection capacity requirements.
Chair(s): Prof. Ioannis Moscholios (University of Peloponnese, Greece)
15:30 - Adaptive Modulation of DCO-OFDM for Internet of Underwater Things Using VLC
Kidsanapong Puntsri (Rajamangala University of Technology Isan, Khonkaen Campus, Thailand); Jariya Panta (Ubon Ratchathani Rajabhat University, Thailand); Wannaree Wongtrairat (Rajamangala University of Technology Isan, Thailand); Bussakorn Bunsri (Rajamangara University of Technology Isan, Khonkaen Campus, Thailand); Muhammad Ijaz (Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
This paper presents an adaptive modulation of direct current-biased optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (DCO-OFDM) for Internet of underwater things (IoUT) using visible light communications (VLC). The adaptive was aimed to reduce bit error rate (BER). The signal to noise ratio (SNR) is monitored, where each symbol is separated into eight SNR groups. The modulation order is adapted according to the SNR gain. In addition, pilot-based is used to measure the SNR. Binary phase shift-keying (BPSK), 4-quadrature amplitude modulation (4-QAM) and 16-QAM with various fast Fourier transform (FFT) sizes are considered. Numerical simulation using Matlab is used. The results showed that the modulation order can be well adapted according to achieve SNR. Additionally, the large FFT size is increased, the bit error rate is slightly decreased.
15:45 - Maximizing Data Rates: A Novel IRS-NOMA Cooperative System for IOT Networks
Mukkara Prasanna Kumar (SRM University AP, India); Sunil Chinnadurai (SRM University of Andhra Pradesh, India)
In this paper, we propose an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) -non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) cooperative system, where the users get the signals from the base station with the aid of the IRS and nearby users to enhance the data rates and expand the coverage of IoT networks. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed IRS-NOMA Cooperative system achieves a better sum rate than conventional IRS-OMA and IRS-NOMA systems.
16:00 - Computational Load Offloading Mechanism in a Converged SDN Control Plane in a 6G Network
Irene Lidia Keramidi (University of Peloponnese, Greece); John S Vardakas (Iquadrat Informatica, Spain); Ioannis Moscholios (University of Peloponnese, Greece); Michael D. Logothetis and Christos Verikoukis (University of Patras, Greece)
The evolution towards the emergence of the smart 6th generation of telecommunication networks targets on unprecedentedly transforming the existing network systems. This unparallel transformation relies on being able to serve in zero-latency highly demanding applications and services hosted on a massive number of devices. This new era of telecommunication networks has designated the need to develop innovative solutions that can intelligently manage the systems' resources in order to deal with the intensified requirements. In this work, we propose aload offloading mechanism aiming to efficiently manage the computational resources of a cell free-based 6G network. We also present a novel traffic-engineering model that aims to evaluate the proposed offloading mechanism and we validate the analytical model with numerical simulation results in order to demonstrate its high accuracy. Finally, we examine the system's performance for different parameter values and it is shown that the offloading mechanism has a strong impact on improving the system's service provisioning.
16:15 - Performance Analysis of Slotted ALOHA Schemes for Massive Machine Type Communications
Koki Takahashi, Chen Guanzhou, Mai Mikogami, Yuki Ichimura and Shigeo Shioda (Chiba University, Japan); Taewoon Kim (Pusan National University, Korea (South))
We evaluate the performance of three slotted ALOHA schemes for mMTC: simple slotted ALOHA without power control or NOMA, slotted ALOHA with power control for solving the near-far problem, and slotted ALOHA with NOMA for increasing the performance gain. Numerical results show that the near-far problem impairs fairness in terms of transmission success probability when neither power control nor NOMA is applied. The application of power control solves the near-far problem, but the performance of slotted ALOHA degrades significantly. The application of NOMA to slotted ALOHA may solve the near-far problem, but the unfairness due to the near-far problem arises again when the number of target values for the received signal strength increases. These results indicate that there is an unavoidable trade-off between fairness and performance gain for slotted ALOHA.
Chair(s): Prof. Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
17:00 - VLC with PV-Based Optical Receiver for Motion Tolerant Optical Axon
George-Iulian Uleru (Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, Romania); Mircea Hulea (Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi, Romania); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Optical axons with visible light communication (VLC) can be used to connect areas of spiking neurons that are in relative motion to each other. In electro-optical-based spiking neural network the parallel transmission of the spikes generated by many neurons is achieved by multiplexing of optical signals. Alternatively, serial transmission of the optical pulses is possible if the activation rate of the neurons permits additional delays. In low-speed VLC systems, an energy efficient photovoltaic panels (PVs) could be used for energy harvesting and data reception (i.e.,photodetectors). In this work, we report a multi-input optical axon VLC link with PV-based receiver and evaluate its performance in terms of the bit error rate (BER) when PV panel powers the SOMAs of the neurons at the transmitter side. The results show that with power harvesting BER varies between 16% and ~40% when the channel length and misalignment are in the ranges 5 - 15 cm, and 0 - 60 degree, respectively.
17:15 - Modelling Optical Wireless Communication for In-Body Communications Systems
Syifaul Fuada, Mr. (University of Oulu & Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Finland); Mariella Särestöniemi (University of Oulu & Research Unit of Health Sciences and Technology and Center for Wireless Communication, Finland); Marcos Katz (University of Oulu, Finland)
OWC for in-body communication (IBC) remains relatively uncharted territory in modelling and practical experimentation. Currently, modelling on IBC systems using OWC is still rare. In this study, we modelled OWC for IBC systems, focusing on capacity rate estimation. The model considered the 633 nm wavelength and other essential things, including the photodiode's active area, responsivity, dark current, circuitry resistance, and bandwidth, in order to estimate the optical link performance based on the Shannon capacity rate across tissue depths ranging from 1to 5 cm. We referred to the model available from the Biophotonics website as the coefficients for tissue properties. We tested our model by inputting parameters available from commercial photodiodes. It is shown that the capacity rates on IBC systems using OWC can reach ~8 Mbps. To simplify the process of estimating the achievable capacity rates at various tissue depths, we also provided the first version of a Matlab-based graphical unit interface (GUI) with the feature included an option to upload optical properties corresponding to the wavelength used. Users could input crucial parameters related to the photodiode profile using this GUI. The GUI provided detailed information on calculating received optical power, photocurrent, noise levels, and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
17:30 - A Feasibility Study of Optical Wireless-Based Data and Power Transfer for In-Body Medical Devices
Syifaul Fuada, Mr. (University of Oulu & Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Finland); Malalgodage Amila Nilantha Perera (University of Oulu, Finland); Mariella Särestöniemi (University of Oulu & Research Unit of Health Sciences and Technology and Center for Wireless Communication, Finland); Simone Soderi (IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, Italy); Marcos Katz (University of Oulu, Finland)
This paper demonstrates the feasibility of transmitting data and power simultaneously through a single near-infrared (NIR) beam across biological tissue. Our study relies on experimental work under the test-bed, constructed from off-the-shelf components. Our study considered an 810 nm375 mW NIR LED, a commercial monocrystalline indoor photovoltaic (PV) cell, a 0.52F supercapacitor for energy storage, and utilized a 15 mm thick pure fat porcine tissue sample. The results indicate that a data speed of 95.7 kbps can be achieved using Gaussian minimum shift keying (GMSK) modulation. The PV cell is employed to harvest energy from the same NIR light source and placed close to a photodetector amplifier (PDA) module; the output of the PV cell is connected to a power management integrated circuit (PMIC) operating within a voltage range of 1V - 4.5V. The supercapacitor can be fully charged under 500 mA of LED current within approximately 41 minutes. The result of this study is promising, as the combination of wireless charging and communication links using an optical-based approach for various IMDs pave the way for future clinical application advancements.
17:45 - Investigation of Suitable MAC Protocols for Optical Wireless Body-Area Networks
Christos Giachoudis and Ali Khalighi (Ecole Centrale Méditerranée, France); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Vasilis K. Papanikolaou (Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany); Sotiris A. Tegos and George K. Karagiannidis (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece)
We consider the use of the optical wireless data transmission from the medical nodes in wireless body-area networks (WBANs) for monitoring a patient's vital signs. To investigate efficient medium-access control (MAC) protocols, we contrast the two developed standards of IEEE 802.15.6 and IEEE 802.15.7 from the points of view of energy efficiency and latency. The first standard was originally developed for radio-frequency signal transmission. The comparison of the two protocols is made using the Castalia simulator and the realistic optical WBAN channel models from a previous work.
Chair(s): Prof. Rafael Perez-Jimenez (IDeTIC, Las Palmas University of Technology, Spain)
17:00 - SNR Analysis for Non-Line-Of-Sight MIMO Optical Camera Communications
Shivani Rajendra Teli (Czech Technical University, Czech Republic); Vicente Matus (IDeTIC-ULPGC, Spain); Satish Kumar Modalavalasa (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
In this paper, we experimentally demonstrate the interference analysis of a non-line-of-sight (NLOS) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)-based optical camera communications (OCC) link. We propose a NLOS MIMO-OCC using two OLEDs and a camera as the transmitters (Txs) and the receiver, respectively, as well as reflections from plain wall and paper surfaces. We analyze the performance of the proposed scheme when two OLED Txs are modulated in out of phase and at different transmission frequencies fs. We conduct an experimental investigation of the proposed system in an indoor environment and evaluate its performance in terms of signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio and the reception success rates Rrs with respect to camera exposure time, the analog gain and varying fs. The initial results depict that at a link span of 2 m Rrs of 100% at the SNR value sof (i) ~5 dB at fs of 100 and 200 Hz; and (ii) ~4 and ~6 dB for OLED1 at fs1 of 100 Hz and OLED2 at fs2 of 200 Hz.
17:15 - Self-Clocking, Constant-Power, Multi-Level Scheme for Optical Camera Communication
Vicente Matus (Instituto de Telecomunicações Aveiro, Portugal & IDeTIC, University Of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain); Atiya Fatima Usmani (University of Aveiro, Portugal); Monica Figueiredo (Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Portugal); Pedro Fonseca (University of Aveiro & Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain); Luis Nero Alves (DETI, Universidade of Aveiro, Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal)
Self-clocking line codes are commonly used in Optical Camera Communication (OCC) links to ensure accurate synchronization of data transmission without the need for an explicit clock signal. In OCC links where the light is used both for illumination and communication, some of these codes (e.g., Manchester) can also help minimize the perceptibility of flickering by ensuring rapid transitions and a consistent signal pattern. When considering multi-level line codes, the same self-clocking and constant power characteristics are desirable, which has led to the recent proposal of a Constant-Power Pulse Amplitude Modulation (CP-PAM) scheme for OCC. However, much like in Manchester coding, there is a significant trade-off associated with its use - the overall spectral efficiency is cut in half. This paper presents an alternative multi-level coding scheme that offers the same self-clocking and similar constant power properties, with a significantly improved spectral efficiency compared to CP-PAM. Experimental results showcase its merits when used in a multi-level sub-pixel OCC link.
17:30 - Optical Camera Communication Based on Side-Emitting Fibers Using Wavelength Division Multiplexing
Klara Eollos-Jarosikova (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Carlos Guerra-Yánez (Czech Technical University, Czech Republic); Vojtech Neuman, Stanislav Zvanovec and Matej Komanec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
Optical camera communication (OCC) using side-emitting fibers offers new transmission possibilities, as side-emitting fibers gradually emit light along the fiber length, thus acting as a distributed light source. In this paper, we explore side-emitting fiber-based OCC architecture, focusing on the integration of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). WDM enabled us to achieve simultaneous transmission of two data streams over a single 1-m long side-emitting fiber, effectively doubling data throughput. Results indicate successful data transmission with minimal bit error rates (BER) under the forward error correction (FEC) limit of 3.8e-3, demonstrating the potential of side-emitting fibers and WDM in enhancing OCC systems by adding additional transmission channels.
17:45 - Data Detection Technique for Screen-To- Camera Based Optical Camera Communications
Vaigai Nayaki Yokar (University of Bristol, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Hoa Le Minh and Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Wai Lok Woo (Northumbria University & Newcastle University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
This paper proposes a data detection technique for screen-to-camera based on visible light communication system. In this system, the image is transmitted utilizing the transmitter screen to be captured and decoded by the receiver smartphone camera. The region-of- interest extraction is carried out on the received image followed by grayscale conversion, edge detection, pixel grouping, Hough and projective transform. The proposed method is implemented in the android platform at different link span, tilt, and rotating conditions. The results indicate that the introduced data detection algorithm, improved the overall detection rate to ~98%.
Chair(s): Prof. Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile)
17:00 - Evolution of OWC: A Collaborative Contour Across Various Sectors
Satish Kumar Modalavalasa (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Atiya Fatima Usmani (University of Aveiro, Portugal); Atiyeh Pouralizadeh Gelehpordesari (Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute, Germany); Christos Giachoudis (Ecole Centrale Méditerranée, France); Luis Miguel Giraldo (Universitat de Valencia, Spain); Raul Zamorano-Illanes and Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Volker Jungnickel (Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute & Technische Universität Berlin, Germany); Ali Khalighi (Ecole Centrale Méditerranée, France); Luis Nero Alves (DETI, Universidade of Aveiro, Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Joaquin Perez (Universitatde Valencia, Spain); Pedro Fonseca (University of Aveiro & Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal)
Wireless optical communication (OWC), has been proposed as a potential technology for applications where the legacy radio frequency (RF) communication may not be suitable or cannot provide the required quality-of-service or security. The OWC has proven its dominance in a widerange of applications where demand for cost-effectiveness, high bandwidth, and relatively high security are predominant. In particular, it has been playing a significant role in ground-to-space, and space-to-ground communications, and is emerging as a viable system for last-meter and last-mile access networks. The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of several of these application areas, which are referred to as sectors.
17:15 - On the Reshape and Comparison of Medium Access Strategies for Infrared Indoor Uplink
Anna Maria Vegni (Roma TRE University, Italy); Valeria Loscrí (Inria Lille-Nord Europe, France); Mauro Biagi (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy)
In the framework of indoor optical wireless communications, a lot of attention has been paid to the downlink, usually implemented via the new paradigm of Visible Light Communication (VLC). On the other side, the uplink communication process is often dropped and the access in uplink is usually performed by other available wireless technologies, such as the Radio Frequency (RF). In this work, we analyze and compare the performance offered by different access approaches in the context of uplink infrared (IR) communication. Specifically, we consider traditional Time Division Multiple Access, ALOHA and Carrier Sensing Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance approaches, potentially reshaped for IR indoor scenario. Indeed, due to the mainly line-of-sight propagation features of the optical wireless channel, CSMA/CA is rephrased so as to work due to the impossibility of users of applying a true (RF-like) sensing mechanism. We report the performance in terms of efficiency and access probability by considering the impact of different parameters as channel capacity, number of users and burstiness of the services/applications.
17:30 - Comparing Models and Approximations of Beam Wander
Mate Galambos (Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary); Giulio Cossu (Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna University, Italy); Ernesto Ciaramella (Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna, Pisa, Italy)
Free space optical communication is a new and promising area with many desirable properties. However, there is no standardized way to model losses and effects of the atmosphere on the propagating beam. This necessitates comparing different models and approximations that are widely used in the literature. We calculate and compare various aspects of beam wander under realistic scenarios. We compare two formulas for the one axis RMS tilt and conclude that they give approximately the same answer under a wide range of scenarios including various optical turbulence models. We also examine the effects of neglecting the Earth's curvature which is an approximation in multiple influential papers. We modify existing equations in the literature to assume a perfectly round Earth. We also examine the beam wander in case of adaptive optics. We conclude that neglecting the curvature introduces no meaningful error when the beam wander is expressed as an angle but can significantly affect the beam wander induced beam displacement expressed in meters. The error is more prominent for GEO satellites and can be meaningful even at small zenith angles.
17:45 - Effects of the Multiplicative SPAD Noise on the Diffusion Adaptive Networks with Noisy VLC Links
Ehsan Mostafapour (University of Urmia, Iran); Changiz Ghobadi and Javad Nourinia (Urmia University, Iran)
The visible light communication technology has been gathering attention recently and as the emerging systems and appliances in this technology are still new, their behavior and performance issues must be taken into the consideration as much as possible. This paper aims to fully model the noise that is emanating from the usage of the Single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) in the VLC systems. This noise is either modeled with the sub-Poisson or Gaussian plus sub-Poisson distributions. These noise models are then applied to the diffusion adaptive networks to show the real-world impact of the VLC noisy links on their performances. The radio noisy link impacts have been investigated on the performance of the diffusion adaptive networks, however, the effects of the optical link noise on their performances is the contribution of this paper. Also, using the realistic and precise models for the optical noise is another novelty in this paper.
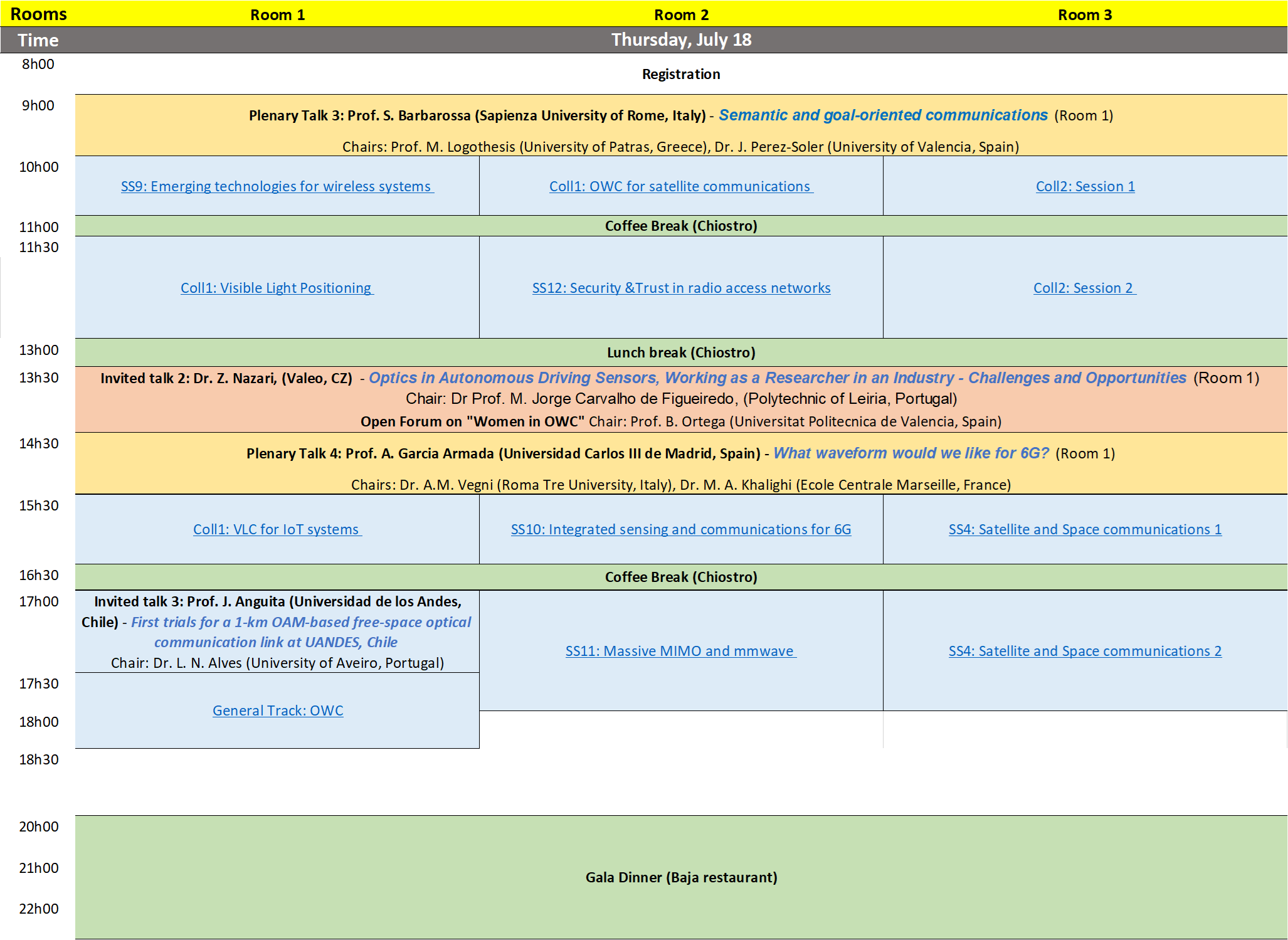
Thursday 18th July 2024
Chair(s): Prof. Michael D. Logothetis (University of Patras, Greece), Prof. Joaquin Perez (Universitat de Valencia, Spain)
09:00 - Semantic and goal-oriented communications
Prof. S. Barbarossa (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy)
The goal of this talk is to illustrate the potentials of a paradigm shift from the conventional Shannon-based approach to semantic and goal-oriented communications. The first part of the talk is devoted to the design of a goal-oriented communication network based on the information bottleneck (IB) method, as a principled way to identify and transmit only the relevant information with respect to the goal of communication. The IB principle is then exploited to derive a communication architecture that adapts the transmission data rate as a function of key performance indicators tuned to the application underlying the data communication. The rest of the talk is devoted to the use of probabilistic diffusion models as a way to design communication systems where the receiver, rather than tryng to recover all the transmitted bits used to encode a semantic message, regenerates a message that is semantically equivalent to the transmitted one. This approach provides many additional degrees of freedom that can be exploited to improve the effectiveness of wireless networks
Chair(s): Prof. Hoa _Le-Minh, Northumbria University, UK
10:00 - Application of B-Delta and UrEDAS on Seismometer Sensor Data to Model the Uncertainty in Time-Critical Detection of Earthquakes Affecting Turkish High Speed Railways
Siamak Tavakoli (Maharishi International University, USA); Abdullah Can Zulfikar (GebzeTechnical University, Turkey)
Since some sections of the Ankara-Istanbul High Speed Railway cross to the North AnatolianFault Zone, it is important to detect the upcoming destructive earthquake before it hits to thetarget. Among few earthquake recognition methods, two methods were identified for investigation on the Turkish earthquake events. Both methods use the first 3 seconds of the vertical component of acceleration signal after the arrival of the P-wave to provide estimates of magnitude and epicentral distance. One method estimates the epicentral distance of earthquakeevents, and the other estimates the magnitude of earthquake. The two methods then take the estimated value to the pre-defined empirical model between magnitude, amplitude, and epicentral distance of the same signal to estimate the other value. This shows that each method requires a valid relationship between magnitude, amplitude, and epicentral distance. Establishment of such empirical models, one per measurement point would require a relatively high number of data series, meaning many earthquake events. To avoid such far-reaching process, this research decided to apply both methods simultaneously on the first 3 seconds ofthe vertical component of acceleration signal after the arrival of the P-wave. The outcome showed a feasible resolution in terms of the detection time.
10:20 - mmW/FSO Based Approach for Target-Detection in Wireless Sensor Networks Under Severe Weather Conditions
Fatima Ibrahim Sharari, Mrs and Mohanad Al-Hasanat (Al-Hussein Bin Talal University, Jordan)
Recently, Free Space Optical (FSO) communication offers advantages over RF in terms of highbandwidth, security, and reliability. However, in contrast to RF links, the efficiency of FSO links is highly susceptible to error in foggy conditions, while it is performance is better in rainy conditions. In this paper, a hybrid RF/FSO communication model is proposed. The proposed model aims at enhancing the reliability and performance of target-detection applications (TD) in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). The model is examined under various weather conditions and at different distances and number of nodes. It is demonstrated that the hybrid scheme surpassed individual RF and FSO schemes via exhibiting lower error rates and better target detection, particularly in adverse conditions.
10:40 - A Survey of Limitations and Future Directions of Antenna Design for UAV Applications
Amjaad Altakhaineh, Sarah Alsarayreh and Rula S Alrawashdeh (Mutah University, Jordan); Khaled M. Rabie (Manchester Metropolitan University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Fatima Ibrahim Sharari, Mrs (Al-Hussein Bin Talal University, Jordan)
Recently, the interest in Areal Unmanned Vehicles (UAVs) has significantly increased which is mainly due to their important and appealing applications including disaster detection and management. UAVs are usually equipped with antennas in order to send or receive data wirelessly. Efficient antennas are essential for robust and continuous communication between the UAV and other devices across various operational scenarios. Different antennas have been already proposed for UAVs. However, they have a number of limitations and shortcomings. In this paper, antennas used in UAVs are reviewed. Challenges and requirements for the antenna designand performance are outlined. Moreover, popular antenna types are surveyed with a focus on highlighting their existing shortcomings and exploring potential future directions. This paper sheds light on the specific requirements necessary for antennas in early warning systems which have not been frequently discussed in literature.
Chair(s): Prof. Joaquin Perez (Universitat de Valencia, Spain)
10:00 - Investigation of Hardware Equalizer Based on a Bridged-T Network for High-Speed VLC
Siti Hajar Ab Aziz (Universiti Kuala Lumpur & British Malaysian Institute, Malaysia); Norhanis Aida M. Nor (International Islamic University Malaysia, Malaysia); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec and Jan Bohata (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
This paper presents a comprehensive investigation of a bridged-T pre-equalizer circuit (BTEC) designed for a high-speed visible light communication (VLC) system. The circuit is intended to mitigate the bandwidth limitation of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in the VLC system. We integrate the advanced design system (ADS) and MATLAB to analyze the BTEC using scattering parameters S11, S12, S21, and S22. The BTEC is fabricated using standard flame retardant type-4 printed circuit boards (PCBs) with a 4.5 x 1.5 mm2 size. The measurement shows that the pre-equalizer centre frequency is similar at 654 MHz for all test sets but with varying dynamic magnitude gains in the range of -9.49 to -33.4dB. The designed BTEC demonstrates that the bandwidth of LED can be extended to provide a solid foundation for future investigations into this area.
10:15 - OCC Strategies for Intra-Satellite communications. OCC4SAT Project
Jose Rabadan (ULPGC, Spain); Victor Guerra (Pi Lighting, Switzerland); Francesco Ferrari (ARGOTEC, Italy); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (IDeTIC, Las Palmas University of Technology, Spain); Marco Giuliani (ARGOTEC, Italy); Benoit Bataillou (Pi-Lighting, Switzerland); Serge Nicolle (ERECA, France)
The current paradigm for intra-satellite communication links is to transfer data via a traditional harness (cabling, connectors, and shielding to ensure Electro-Magnetic Compatibility). This translates in a percentage of the cost of the satellite, since more dry mass leads to increased required propellant, producing an even larger increase of the total launch mass and thus the mission cost; moreover, the harness can also cause problems in the design and integration phases. OCC4SAT project propose to tackle some of these problems by employing the Optical Camera Communication (OCC) technology, which uses optical cameras instead of photodiode-based detectors to receive the optical signal, to substitute the low data-rate harness in spacecraft. With this technology, it is feasible to achieve a data-rate of a few kbps within expensive COTS components. Light can travel through small gaps and undergo multiple reflections and still be received, due to the increased sensitivity of optical camera sensors compared to photodiodes, leading to lower power consumption and more relaxed emitter configuration constraints. This allows for great flexibility in the link architecture, ease of adaptation to design changes, and mass and cost reductions.
10:30 - On the Use of Lightwave Power Transfer in Miniaturized Satellite Communication Systems
Nikolaos Kyriatzis, Dimitrios Gkiaouris and Sotiris A. Tegos (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece); Panagiotis Diamantoulakis (University of Western Macedonia, Greece); Vasilis K. Papanikolaou (Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany); Robert Schober (Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany); George K.Karagiannidis (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece)
CubeSats have a significant impact on the satellite communications sector due to their ability to provide rapid, cost-effective, and adaptable improvements to existing satellite networks or to individual missions. The main challenge facing CubeSats is their energy sustainability. Towards this end, we are considering Optical Wireless Power Transfer (OWPT) technology from larger satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) as an alternative power source for CubeSats. We propose a strategy that involves the simultaneous harvesting of CubeSat energy and the establishment of a communication link to a Ground Base Station (GBS). We formulate an optimization problem for the proposed strategy, aiming to maximize the average data rate on the communication link.
10:45 - Cymatics and Their Potential Applications in Free Space Optical Communications
Alex Cameron (University of Northumbria, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Mojtaba Mansour Abadi (Industry Supervisor, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Zabih Ghassemlooy and Richard Fu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Free space optics (FSO) is seen as a complementary wireless technology to radio frequency technology (RF) for applications in high-speed and long-distance communications. Although it surpasses traditional RF-based communications with its higher data rates and increased security to create a scalable communication infrastructure, it has certain drawbacks, which must be adequately addressed before it becomes a norm for terrestrial communication. One of the major issues it faces is the effect atmospheric weather conditions such as fog, rain and turbulence that can attenuate the encoded light leading to the performance degradation. While modal vibrational phenomena have been studied for some considerable time, cymatics and the visualisation of sound waves could be the key to the future of FSO. Primarily due to the modal frequencies having a significantly higher interaction rate with droplets or particles than others. This paper outlines the process of identifying these frequencies and presents experimental results outlining their applications in the path clearing in the FSO links.
Chair(s): Prof. Qiang Wu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
10:00 - Optimal Few-Mode Self-Similar Pulse Compression in Photonic Crystal Fibers
Liu Baojun and Jinhui Yuan (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China); mei chao (University of Science and Technology Beijing, China)
In this paper, few-mode self-similar pulse compression in tapered photonic crystal fibers (TPCF) is proposed and optimized. Simulation results show that for 1.55-ps input pulse, self-similar pulse compression with > 10 factor can be realized simultaneously for three modes in 1.9-m TPCF.
10:12 - Mid-Infrared Broadband Polarization Beam Splitter Based on GaS Photonic Crystal Fiber
Jilu Li (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunication, China); Jinhui Yuan and Yuwei Qu (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China); Binbin Yan and Kuiru Wang (Beijing University of Post and Telecommunication, China); Qiang Wu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
A mid-infrared polarization beam splitter (PBS) based on GaS dual-core photonic crystal fiber (DC-PCF) with large bandwidth is proposed. The numerical simulation results indicate that when the incident light wavelength is chosen as 4.5µm, the splitting length is 150.9µm, the maximum extinction ratio of 75.51dB, and the working bandwidth is up to 285nm (4.354-4.639µm).
10:24 - A Polarization Beam Splitter Based on Dual Hollow-Core Anti-Resonant Fiber with High Extinction Ratio and Large Bandwidth
Guoqing Zhou and Jinhui Yuan (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China); Kuiru Wang and Binbin Yan (Beijing University of Post and Telecommunication, China); Qiang Wu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Guiyao Zhou (South ChinaNormal University)
A polarization beam splitter based on a dual hollow-core anti-resonance fiber structure is proposed. The optimal propagation length of the polarization beam splitter is 2.36 cm, and the bandwidth is 550 nm (1330-1880 nm). It can achieve a maximum extinction ratio of 86 dB. Furthermore, it has good single-mode transmission characteristics. The polarization beam splitter has a good beam splitting effect in the whole communication band. It will have significant applications in the optical communication and sensing systems.
10:36 - Birefringent Frequency-Scanning Phase-Sensitive OTDR Based Fiber-Optic Hydrostatic Pressure and Temperature Sensor
Huan WU (Research Assistant Professor, Hong Kong); Hua Zheng (Associate Professor, HongKong); Yuyao Wang, Xinliang Shen, Zheng Fang and Chao Lu (The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong)
In this paper, we propose a highly sensitive distributed optical fiber sensor capable of simultaneous hydrostatic pressure and temperature sensing. By demodulating both the frequency shift of Rayleigh scattering and birefringence of the polarization maintaining fiber (PMF), a sensorwith 10 kPa hydrostatic accuracy and 66.5 mK temperature accuracy is demonstrated.
10:48 - Cascaded Optical Fiber Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Ultraviolet Irradiance and Temperature
Qiang Wu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Ru-Lei Xia, Juan Liu, BinLiu and Xingdao He (Nanchang Hangkong University, China); Hau Ping Chan (City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong); Jinhui Yuan (University of Science & Technology Beijing, China); Zabih Ghassemlooy and Xicong Li (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Qiao Gao and Yingying Hu (Nanchang Hangkong University, China)
A new cascaded optical fiber sensor, which can measure Ultraviolet irradiance and Temperature simultaneously was designed and verified by experiment, which consists of an extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer (EFPI) with benzocyclobutene (BCB) and a few-mode fiber Mach Zehnder interferometer (MZI). By performing a Fourier transform and applying a frequency domain bandpass filter, the polymer-EFPI and few-mode fiber MZI spectra were separated from superimposed spectra of cascaded structure. The sensing characteristics of temperature and ultraviolet (UV) irradiance were tested and analyzed in detailed, respectively. By constructing a sensitivity matrix, the difference in sensitivity between MZI and EFPI can be used to make simultaneous measurements of temperature and UV irradiance. The UV irradiance and temperature sensitivities are 0.0039 nm/(mW/cm2) and 0.2021nm/°C, respectively. In addition, the cascaded structure is insensitive to the change of ambient refractive index (RI), which can effectively avoid the cross-interference of RI. The new optical fiber sensor is more stable, requires a simpler manufacturing process and can be produced at lower cost when compared to existing sensors. The new optical fiber sensor can also be applied to multi-parameter applications, reducing the complexity of the deployed system.
Chair(s): Dr. Shivani Rajendra Teli (Czech Technical University, Czech Republic)
11:30 - A YOLOv5 and Improved Perspective-4-Points Algorithm Based Indoor LOS and NLOS Adaptive Visible Light Positioning System
Jingxian Yang (Fuzhou University, China); Weijie Huang (Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, China); Yongqi Ding (Chinese Academy of Sciences, China); Jiabin Luo (Quanzhou Institute of Equipment Manufacturing, Haixi Institutes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China); Hongtao Yu (FuZhou University, China); Shujie Yan (Fuzhou University, Singapore); yixianghuang (Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, China); Bangjiang Lin (Quanzhou Institute of Equipment Manufacturing, Haixi Institutes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Visible light positioning systems (VLPs) that are based on line-of-sight (LOS) are highly accurate; however, they cannot operate under shadowing/blocking conditions commonly encountered in indoor environments. Relaying on non-line-of-sight (NLOS) transmission paths can resolve this problem at the cost of poor performance. In this paper, we propose an indoor LOS and NLOS adaptive VLP system that overcomes shadowing/blocking and maintain a high level of performance. To achieve dynamic algorithm switching and position estimation, the proposed system uses an improved perspective-4-points (P4P) algorithm. Further, a deep learning (DL)model, YOLOv5, is designed to detect the highlight spots formed by light emitting diodes (LEDs) over LOS or NLOS paths due to its improved accuracy and generalization. Experimental results show that the proposed system can provide a good three-dimensional positioning accuracy, with mean square errors of 13.2 cm for LOS and 28.1 cm for NLOS, respectively.
11:48 - Evaluation of Machine Learning Models for Received Signal Strength Based Visible Light Positioning with Obstacles
Jorik De Bruycker (KU Leuven, Belgium); Michiel De Wilde and Federico Garbuglia (Ghent University, Belgium); Ioana Nikova (Ghent University & Siemens Industry Software, Belgium); Ivo Couckuyt (Ghent University, Belgium); Tom Dhaene (Ghent University & IMEC, Belgium); Nobby Stevens (KU Leuven, Belgium)
Received Signal Strength based Visible Light Positioning (RSS-VLP) is an attractive solution for indoor positioning as an enabling technology for future smart environments. Despite this significant importance, there is currently no research focus on the influence of obstacles in the environment. Obstacles could prevent the mobile unit from reaching certain locations, or altogether block the line of sight between the receiver and the light sources. Therefore, this work compares the performance of different machine learning models for visible light positioning using a simulated environment where obstacles can be added. The results shows that machine learning models require much more training data to achieve acceptable performance when shadowing occurs. Gaussian Processes show the best performance out of all evaluated models in environments both with and without obstacles. However, the optimal attainable performance degrades when shadowing is introduced.
12:06 - Deployment of Visible Light Positioning Techniques at Low Data Rate for V2V Industrial Communications
Luis Miguel Giraldo and Joaquin Perez (Universitat de Valencia, Spain); Carmen Botella-Mascarell (University of Valencia, Spain); Sandra Roger (Universitat de València, Spain); Vicent Girbes (Universitat de Valencia, Spain); Raimundo Garcia (Department of Electronic Engineering - Higher Technical School of Engineering, Spain); Jordi Sansaloni Giner(PROEMISA S. L, Spain)
The analysis and implementation of a reliable setup facilitate direct linkage between visible light communication (VLC) and various encoded identifiers serving as informational beacons to test vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication systems for positioning applications. This designed system enables LED panel control and establishes a protocol for managing communication between LED luminaries and the receiver. Test-bed requirements have been assessed and applied to anticipate future scenarios of optical wireless communication for V2V applications. Analysis of the results indicates the potential use of commercial outdoor luminaries in V2V positioning scenarios, even under daylight conditions, with a data rate of 100 Kbps. Additionally, the successful detection of positioning beacons aids vehicle localization within relevant operational regions for prospective V2V applications.
12:24 - Analysis of a Visible Light Positioning Database in Extreme Learning Machines Applications
Benjamín Lobos Soto (Universidad Católica del Maule, Chile); Cesar Azurdia (Universidad de Chile, Chile); David Zabala-Blanco (Universidad Católica del Maule, Chile); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile); Pablo Palacios Játiva, Dr. (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile); Roberto Ahumada García (Universidad Católica del Maule, Chile)
Over the past few years, there has been a growing interest in indoor positioning systems that use Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology in conjunction with light-emitting diodes (LEDs). These systems have become popular because of their ability to provide high bandwidth, and it is anticipated that wireless communication may expand into the visible-light spectrum in the future. This makes VLC a promising option for high-speed line-of-sight communication. Additionally, the visible light spectrum can be deployed in the Industrial Internet of Things environment, as it does not emit electromagnetic radiation and is immune to electromagnetic interference. This article presents a database consisting of an average of 356 image samples obtained from a CMOSsensor. This database includes seven different classes, each class varying its frequency from 1kHz to 4.5 kHz with a 500 Hz interval. The goal is to apply this database to various neural networks based on Extreme Learning Machines (ELM) in its variants: MATLAB environment was used to evaluate the performance of the proposed indoor positioning system enabled for VLP. Our results indicate that a promising option is standard ELM since it has a performance greater than 99% accuracy and mean G, and low computational complexity compared to CNN.
12:42 - Performance Evaluation of Spatial Modulation in A Hybrid Variable m-CAP-Based Indoor Visible Light Communications and 3D Positioning System
Atiyeh Pouralizadeh Gelehpordesari, Mahdi Nassiri and Gholamreza Baghersalimi (University of Guilan, Iran)
A combination of spatial modulation (SM) and variable multi-band carrier-less amplitude and phase (m-CAP)-based indoor visible light for data communications and positioning is evaluated. The fingerprinting algorithm for 3D positioning is considered. The link performance in terms of the bit error rate (BER) and the positioning error (PE) are examined for a range of Eb/N0's. Based on the results, for a fixed step size of 5cm and a 7% forward error correction (FEC) BER limit of 3.8e-3, the best PE value and spectral efficiency (SE) are ~4 cm and 3.07b/s/Hz, respectively. Also, it has been shown that for a fixed step size, PE decreases with increasing Eb/N0.
Chair(s): Dr. Dimitrios Pliatsios (University of Western Macedonia, Greece)
11:30 - Accelerating AES in 5G Security Protocols: A System-Level FPGA Implementation
Kunhuan Xu and Dongshan Ye (School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-Sen University, China); Xiang Chen (Sun Yat-Sen University, China); Xijun Wang (Sun Yat-sen University, China); Zhigang Tian, Chunsheng Shen and Ming Zhao (Tsinghua University, China); Song Wu, Jie Liu and Hui Zhi (China Mobile Research Institute, China)
In this research work, we address the necessity of accelerating 5G cryptography and present a Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Implementation of a system-level acceleration scheme for the advanced encryption standard (AES) algorithm in 5G PDCP cryptography. The solution includes the design and implementation of the user-space module, the kernel-space module, and the FPGA module, utilizing a data path based on Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) between the host and the FPGA. Results show FPGA-based acceleration scheme canachieve 35.9 times at most at unit rate tests and improve by 488.75 Mbps at most in the real wireless communication environment compared to the pure C-based implementation.
11:52 - Performance Evaluation of Multi-Gb/s Sub-6 GHz Signals over Bidirectional Microwave Photonic Links for Urban and Rural Areas
Jan Bohata (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Dong-Nhat Nguyen (II-VI Incorporated, Binh Duong, Vietnam); Luis Vallejo (Bangor University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Beatriz Ortega (ITEAM Research Institute, Spain); Jose Mora (Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Spain); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a full-duplex fiber-space-fiber system in the 5G sub-6 GHz frequency bands for simultaneous transmission of multi-Gb/s downlink and uplink signals. In the downlink direction, error-free transmission of a 2.4-Gb/s 64-quadrature amplitude modulation (64-QAM) signal at 5-GHz over a seamless optical link of 10-km standard single-mode fiber (SMF), 1.2-m free-space optics (FSO) and 1.4-km SMF is achieved by using external modulation. In the uplink direction, a directly modulated laser is employed to transmit 2-Gb/s 4-QAM signal at 3.5-GHz over the same hybrid channel with the measured error-vector magnitude(EVM) value satisfying the 3GPP limit. The proposed system provides a practical solution for extension or recovery of broadband wireless connectivity.
12:15 - Code-Aware Anti-Jamming Method for FHSS Systems: Leveraging Diversity Combination
Yuchen Xu, Yunzhu Xian, Jiaxuan Li and Xiangyuan Bu (Beijing Institute of Technology, China); Xuhui Ding (Beijing Institude of Technology, China)
Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) systems exhibit exceptional resilience against jamming through the utilization of time-frequency diversities, which, when coupled with near-Shannon limit channel codes, yield favorable performance outcomes. The coherently combined and decoded signals at the receiver effectively eliminate the impact of partial-band jamming. This letter proposes a novel low complexity low-density parity-check (LDPC) code-aware diversity combining anti-jamming (LCA-DCAJ) method for fast frequency hopping (FFH) systems. Our approach seamlessly integrates multidimensional (time-frequency) diversities, FFH strategies,and LDPC coding techniques, resulting in outstanding suppression of interference within the time-frequency domain. Addressing concerns over complexity, we propose a triple log-likelihood ratio (LLR) threshold detection algorithm to further streamline implementation procedures. Bit error rate (BER) and average processing delay (APD) analyses underscore the superiority of the proposed anti-jamming method, validating its effectiveness in practical scenarios.
12:37 - Evaluating the Performance Open-Source Vulnerability Scanners
Mohammad Rafi Gajula and Vassilios G. Vassilakis (University of York, United Kingdom (GreatBritain))
The increasing complexity of cyber threats necessitates powerful and versatile vulnerability assessment tools. This study evaluates the performance and efficiency of leading open-source cybersecurity scanners - OpenVAS, ZAP, Nessus, Nikto, and Nmap - in various network environments, including sophisticated cloud infrastructures and more constrained local PCsetups. Utilizing platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Linode, the research provides insights into how different environments impact the effectiveness of these tools. A key finding is the significant influence of network resources on the efficacy of scanners, underscoring the critical need for cybersecurity practitioners to consider the specific characteristics of their network environment when selecting tools. Through data collection and analysis, the capabilities of each tool are illuminated, offering valuable guidance for more effective deployment in cyber security practices.
Chair(s): Dr. Othman Isam Younus, Cambridge University, UK
11:30 - Highly Sensitive Label-Free Biosensor Based on Microbottle Cavity-Gold Nanocoated Layer for Facile Detection of COVID-19 RNA
Houchang Li (University of Science and Technology Beijing, China); Jinhui Yuan (University of Science & Technology Beijing, China); Yuwei Qu (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China); Kuiru Wang (Beijing University of Post and Telecommunication, China); Qiang Wu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Bin Liu (Nanchang Hangkong University, China)
To improve the sensitivity of whispering-gallery mode microbottle cavity to the low-concentration solution, a nanoparticle gold film-modified micro-bottle cavity sensor is proposed and demonstrated by measuring low-concentration measurement of RNA virus (COVID-19) molecules. The results show that the refractive index sensitivity of the micro-bottle cavity can be effectively improved by a nano-gold film, which can reach 261 nm/RIU in the refractive index range of 1.3320 to 1.3332. In the concentration range of 10 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL COVID-19 RNA, the sensor output signal has a linear relationship with the concentration, and the detection limit can reach 10 pg/mL. The sensor has high sensitivity and strong stability and has broad application prospects in the field of bio sensing.
11:48 - A Novel Molecular Imprinting Polymer based Optical Fibre Sensor for Valsartan
Haili Ma (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Meng Zhang (Northumbria UNiversity, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Yicun Yao (Liaocheng University, China); Jinhui Yuan (University of Science & Technology Beijing, China); Matthew Unthank and Qiang Wu (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
A novel molecular imprinting polymers (MIPs) based Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) optical fiber sensor for detection of valsartan is designed and demonstrated experimentally. The MZI fiber sensor is fabricated using a traditional thermal tapering method with a taper diameter of 4.5µm and a sensitivity of 1770nm/RIU at the refective index of 1.33. The molecular imprinting polymers (MIPs) is synthesized using high-affinity binding sites via solid-phase based process, where valsartan is used as a target molecule. The sensor is treated utilizing a EDC/NHSS activated process and immobilized with the synthesized valsartan MIPs. Experimental results show that the developed MZI MIPs sensor has a linear response within the valsartan concentration range of 0 to 500pg/mL, with a low detection limit of 35pg/mL.
12:06 - Ring-In-Ring Beam Shaping Based on a 3D Nanoprinted Microlens on Fiber Tip
Chenyang Su, Liu Dejun, Li Zhuorong, Tai Yalong, Huang Ziyi, Bao Wejia, Yiping Wang and Changrui Liao (Shenzhen University, China)
Micro-optical elements have been attracting growing attentions in a large variety of applications,such as telecommunication, sensing technology, and industrial inspection. In this paper, we propose a 3D printed free form microlenses on fiber tip for beam intensity shaping. Femtosecond laser two-photon polymerization (TPP) technic is used for fabrication of the microlens. Both simulation and experiment results have demonstrated that the Gaussian beam output from a single-mode fiber can be successfully transferred to a double-ring beam by using the fiber-tip microlens. The study indicates that TPP provides a new and flexible method for the integration of micro-scaled beam shaping elements on optical fibers.
12:24 - High Sensitive Refractive Index Sensor Based on Dispersion Turning Point Long-Period Fiber Gratings in Tapered Fiber
Meng Wu, Siyu Chen, Yuehui Ma, Xiaolong Fan, Chengbo Mou and Yunqi Liu (Shanghai University, China)
We proposed a high sensitive refractive index sensor based on the long-period fiber gratings inscribed in the tapered fiber at dispersion turning point. The sensitivity of the refractive index sensor can reach 19473.3 nm/RIU.
12:42 - Polymer Optical Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Whispering Gallery Modes
Anand VR (Technological University Dublin); Zhe Wang, Zhuochen Wang, Anuradha Rout, Rayhan Habib Jibon and Yuliya Semenova (Technological University Dublin, Ireland)
This paper reports and experimentally demonstrates a strain sensor based on whispering gallery modes (WGMs) effect in a polymer step-index optical fiber. Excitation of WGMs in polymer optical fiber (POF) is achieved by evanescent coupling with a silica fiber taper. The tensile strain to a short section of a polymer fiber is applied by axial elongation. Our results show that the proposed WGM stain sensor can measure strains up to 6666µe with a strain sensitivity of 0.49pm/µe.
Chair(s): Prof. Monica Figueiredo (Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Portugal)
13:30 - Optics in Autonomous Driving Sensors, Working as A Researcher In An Industry - Challenges and Opportunities
Dr. Zahra Nazari, (Valeo, CZ)
Chair(s): Prof. Rafael Perez-Jimenez (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain), Prof. Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
14:30 - What waveform wouldwe like for 6G?
Prof. Ana Garcia Armada (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain)
The evolution of mobile communications towards 6G will enable new applications and services that require a new radio interface able to meet new key performance indicators (KPIs). These mobile systems should be capable of operating in all kinds of environments, including some challenging ones that were not fully covered with 5G. What new requirements do we have for the waveform and the way the radio resources are organized? These have an enormous impact on the achievability of the KPIs and the ubiquitous provision of mobile services. This talk examines the properties, advantages, and disadvantages of some recently proposed waveforms and advocates that the key ingredient in this evolution is flexibility. Different ways to multiplex the pilots and data in an efficient way are explored as well, together with the option of not requiring any of them via non-coherent demodulation
Chair(s): Prof. Vassilios G. Vassilakis (University of York, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
15:30 - Principal Component Analysis for Robust Region-Of-Interest Detection in NLOS Optical Camera Communication
Maugan De Murcia (Université de Poitiers, CNRS, XLIM, Poitiers, France); Hervé Boeglen (University of Poitiers XLIM CNRS 7252, France); Anne Julien-Vergonjanne (University of Limoges & XLIM CNRS 7252, France); Pierre Combeau (Université de Poitiers, CNRS, XLIM, Poitiers, France)
In Optical Camera Communication (OCC), the transmitted data sent through the brightness variation of a Light-Emitting Diode (LED) is detected by a camera rather than a conventional photodiode. Thus the major issue in the process of recovering the transmitted signal recorded in images is the detection of the Region-Of-Interest (ROI), corresponding to pixels that are actually containing information. To achieve this, the Principal Component Analysis is for the first time to the authors best knowledge, applied to images obtained through rolling shutter effect in order to extract the transmitted signal. Obtained results clearly show an improvement in the robustess of ROI detection compared to other methods, increasing by 60.2 % the achievable communication distance considering a raw Bit Error Rate (BER) of 10 -3.
15:45 - A Packet-Based Analog m-CAP Visible Light Communication System for Internet of Things
Luis Rodrigues (Instituto de Telecomunicações-IT, Aveiro & Universidade de Aveiro, Portugal); Monica Figueiredo (Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Portugal); Luis Nero Alves (DETI, Universidade of Aveiro, Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
The Internet connectivity in electronic devices has been progressively increasing over the years. While radio frequency (RF)-based communications dominate Internet of Things (IoT) applications, they face some issues such as interference and spectrum limitations. Visible light communications (VLC) uses light emitting diodes (LEDs) lights with intensity modulation to convey the signal and it has been demonstrated as a viable alternative for indoor IoT scenarios. On the other hand, data clock synchronization between the transmitter (Tx) and the receiver (Rx) is crucial for reliable data transmission, mitigating timing errors and packet losses. Typical implementations are complex and require high-speed processing. This paper introduces an algorithm for data clock synchronization in a hybrid multiband carrierless amplitude and phase (m-CAP)/quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) VLC system for IoT devices, ensuring accurate clock recovery that can be implemented in a low-cost microcontroller. The system achieves synchronization with a clock mismatch tolerance of up to 4200 ppm, supporting frames with a payload length up to 624 octets. By using averaging window sampling instead of a single sample acquisition, it is possible an extension of the payload length by approximately 208 octets.
16:00 - An SDR-Based Testbed for Extending the Physical Layer of LR-WPAN Architectures Using VLC
Carlos Guerra-Yánez (Czech Technical University, Czech Republic); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
In this work, we present the first steps towards the use of visible light communications (VLC) as an extension of the physical layer of low-rate wireless personal area network architectures for indoor links. We present a testbed using a software-defined radio (SDR) platform, i.e., the ADALM-PLUTO active learning module, to transmit and receive low-rate signals in the VHF bandand a media converter to introduce them in a VLC link. We report error-free detection up to 1m using a lens in the transmitter to reduce the beam width to 5 degrees.
16:15 - Novel Design of Two-Tier Slotted-ALOHA OWC/RF IoT Networks with Adaptive Control
Milica Petkovic (Faculty of Technical Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Serbia); Anna Maria Vegni (Roma TRE University, Italy); Enrique Hernández-Orallo and Pietro Manzoni (Universitat Politècnica de València, Spain); Dejan Vukobratovic (University of Novi Sad, Serbia)
In this work, we present a novel design of a two- tier slotted-ALOHA system for massive Internet of Things (IoT) systems. Indoor IoT devices access the network via optical wireless communication (OWC), and relay data via a back-haul radio frequency low-power wide-area network (LPWAN). The main motivation of system under consideration is to reduce the connection density of LPWANs by offloading indoor devices to the OWC-based IoT. The first OWC tier employs slotted-ALOHA random access protocol with multi-packet reception and capture effect in the presence of interfering users, while the second LPWAN is based on slotted-ALOHA with different slot rates compared to the OWC tier. The aim of the presented analysis is to offer design insights for the two-tier OWC/RF system, while focusing on the adaptive selection of the data rates of OWC and LPWAN networks.
Chair(s): Dr. Daniel Castanheira (Instituto de Telecomunicações (IT)/ University of Aveiro, Portugal)
15:30 - Joint Sensing and Communication with Graphene FETs Targeting Terahertz Band
Monica La Mura and Patrizia Lamberti (University of Salerno, Italy); Alessandro Stuart Savoia (Roma Tre University, Italy); Roberto Alesii and Dajana Cassioli (University of L'Aquila, Italy); Vincenzo Tucci (University of Salerno, Italy)
The upcoming 6G paradigm for wireless communication networks promises enhanced data rates, reduced latency, and pervasive connectivity. In this scenario, the combination of sensing and communication capabilities enables intelligent and adaptive communication protocols and innovative smart sensing systems. This paper introduces the role that graphene technology might cover in the evolving landscape of sensing combined with high-frequency communication, exploring the architectures currently investigated for radiofrequency (RF) electronics and joint sensing and modulation based on graphene field-effect transistors (GFETs). Current challenges and limitations of graphene technology are also discussed.
15:45 - MU-MIMO and Multi-Beam ISAC Hybrid Beamforming Design
Leonardo Leyva (University of Aveiro & Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Daniel Castanheira (Instituto de Telecomunicações (IT) / University of Aveiro, Portugal); Adão Silva (Instituto de Telelcomunicações, Portugal); Atílio Gameiro (Instituto de Telecomunicações / Universidade de Aveiro, Portugal)
This paper addresses the problem of fully-connected hybrid analog-digital (HAD) beamforming design for a multi-user and multi-beam ISAC setup. Traditional approaches to this problem involve a two-step process: first, a fully digital precoder is obtained, then the HAD beamforming is resolved by minimizing the Euclidean distance to the previously designed fully digital precoder. However, the main drawback of this method is that the communication or radio-sensing constraints considered in the first phase may be not preserved after the second one. In contrast, our work prioritizes preserving these constraints by directly designing the fully-connected HAD beamforming. We maximize the weighted sum rate while subject to power budget and radio-sensing constraints. To solve this, we propose an innovative iterative alternate optimization algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate performance close to that of a fully digital precoder, outperforming previous fully-connected hybrid beamforming methods for ISAC.
16:00 - Networked ISAC Coordinated Beamforming and Cooperative BS Cluster Optimization
Kaitao Meng and Christos Masouros (University College London, United Kingdom (GreatBritain))
In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks to optimize and balance the sensing and communication (S&C) performance. Using stochastic geometry, we analyze S&C performance by deriving tractable expressions for area spectral efficiency (ASE), based on which, we optimize cooperative base station cluster sizes for S&C, along with user/target numbers, to achieve a flexible S&C tradeoff. It is shown that interference cancellation significantly improves the average data rate and the radar information rate. Interestingly, optimal communication tradeoffs aimed at maximizing ASE mainly emphasize spatial resource utilization for multiplexing and diversity gain without interference nulling. Conversely, for sensing objectives, resource allocation tends towards interference cancellation. Simulation results confirm that our proposed cooperative ISAC scheme significantly improves S&C performance.
16:15 - Towards Affordable RIS Devices: Electromagnetic Simulation and Implementation of Metasurfaces
Jokin Cifuentes, Joseba Osa and Iban Barrutia (Mondragon Unibertsitatea, Spain); Mikel Mendicute (Mondragon University, Spain)
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces can change their reflective response to adapt to changes in the communication channel, where such response is obtained by modifying the reflection coefficient of each of the unit cells that make up the surface. The paper analyzes, through electromagnetic simulations and actual PCB designs, the viability and performance of four different metasurface configurations, whose implementation has been carried out using standard PCB materials. Four surfaces with fixed reflection response have been used to asses the viability of the proposed schemes and materials for future controllable RIS implementations. Each one of the test designs uses a different element discretization configuration. An analysis via EM simulation and comparison with experimental results has been performed to study the influence of the cell discretization on the response of the surfaces, at 9.6 GHz. The conducted study and the obtained results may be useful for future designs and implementations of adaptive response RIS at higher frequencies.
Chair(s): Prof. Franz Teschl (Graz University of Technology, Austria)
15:30 - A Direct Satellite-To-Underwater LiDAR-Based Communication System
Stefano Mangione. (Università degli Studi di Palermo, Italy); Daniele Croce (University of Palermo, Italy); Federica Poli and Alessandro Ugolini (University of Parma, Italy)
Direct satellite-to-underwater communications are a cutting-edge research frontier for innovative applications, such as real-time oceanographic data collection, disaster response and early warning systems, underwater exploration and mapping, scientific research, marine infrastructure maintenance and security surveillance. However, several challenges must be addressed to fully exploit satellite-to-underwater direct communications. In this paper we propose a model to explore the feasibility of such a direct air-to-underwater optical link for a LiDAR-based satellite communication system, in terms of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The model is inspired by [1], and our results show that it is possible to achieve a good SNR level in absence of direct sunlight, both in the downlink and in the uplink direction. Future work will include possible interference due to sky brightness and moonlight and investigate how to improve the communication performance in presence of direct sunlight.
15:45 - Advancing Off-Road Operations: Comparative Assessment of Object Detection Methodologies
Javier Saez-Perez (University of the West of Scotland, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); JoseMaria Alcaraz Calero (University of the West of Scotland & School of Engineering and Computing, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Qi Wang (University of the West of Scotland, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Jose Garcia-Rodriguez (University of Alicante, Spain)
Off-road operations such as search and rescue or goods delivery in remote wilderness environments demand efficient and effective strategies to locate individuals. Traditional Search and Rescue (SAR) methods, such as canine units and human-assisted search, face challenges in timeliness, cost, scalability and adaptability. To address these limitations, we explore the integration of ground robots equipped with LiDARs into SAR workflows, focusing on off-road scenarios where adverse weather or complex terrain hinder conventional methods like Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Our study conducts a comprehensive analysis of single-sensor LiDAR algorithms for small object detection in off-road environments, utilizing a newly curated dataset tailored for SAR applications. We identify the critical role of sensor configuration and environmental factors in detection performance, providing insights for designing robust detection systems. By filling gaps in existing literature and elucidating the strengths of single-sensor LiDAR algorithms, we contribute to advancing off-road operations methodologies and technology. Our findings underscore the potential of integrating ground robots into off-road operations and offer valuable guidance for enhancing search capabilities in challenging environments.
16:00 - Enhanced Energy Aware and Void Avoidance Routing Protocol Based on Vector Based Forwarding for Underwater Acoustic Wireless Sensor Network
Muhsin Hassanu (University of Salford, Manchester, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Almost seventy one percent of the earth is covered with water, making it crucial to human survival. Over the years, monitoring, and discovery of natural resources such as salt, crude oil etchas increased the importance of the oceanic world. With the rapid growth of technology, the discovery and monitoring of natural resources in the water has led to autonomous communication that gives rise to internet of underwater things. One of the major challenges faced by the underwater sensor network is sensor nodes mobility and energy constraint as the nodes are powered by limited battery resources which makes it quite difficult to replace or recharge once deployed. Routing is essential for the sensor nodes to exchange information and transmit data from source to destination. To address this issue, an energy efficient routing protocol is crucially required. Hence, this paper proposes an underwater energy efficient and void avoidance routing protocol named enhanced vector-based forwarding (ENHVBF) which examines the energy of the sensor nodes for successful communication. AQUASIM-NG simulator for NS-3 was used in measuring the performance of ENHVBF. Result obtained show an improved performance for ENH-VBF in terms of energy consumption and packet delivery ratio when compared with other routing protocols
16:15 - Hybrid Model for Estimating State of Charge of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Carlos Fernandez-Grandon (Universidad de Santiago, Chile); Wilson Alavia (Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile)
The objective of this study is to develop hybrid models to estimate the state of charge (SoC) of lithium-ion batteries (LiB). An LiB dataset from Bayerische Motoren Werke (BMW) i3 60Ah containing physical variables such as voltage, current, and temperature was studied, and a fourth variable was derived, which was the charge obtained by integrating the current over time. The parameters of the equivalent circuit of an RC branch (ECM1RC) were estimated, and Machine Learning (ML) models were trained and evaluated for regression, such as the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM), Decision Tree (DT), and a combination of these, through hybrid and ensemble models and through Linear Regression (LR) to increase the individual performance of the models. After 5 folds of cross-validation and subsequent testing on a Raspberry Pi 4, a fitting curve (R^2) of 0.9999 and RMSE of 0.0018% were obtained for the ECM1RC+DT hybrid model using 100,232 testing data. In addition, using the same models retrained using the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) 18650 LiB data, an (R^2) of 1.0, and an RMSE of 0.0% were obtained for the ECM1RC+DT using 201,501 testing data.
Chair(s): Prof. Luis Nero Alves (DETI, Universidade of Aveiro, Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal)
17:00 - First trials for a 1-km OAM-based free-space optical communication link at UANDES, Chile
Prof. J. Anguita (Universidad de Los Andes, Chile)
We describe a new laser transmission cabin built at Universidad de los Andes for long-term experiments in the classical and quantum domains, using spatial diversity by means of orbital angular momentum (OAM) and double apertures for single-photon transmission. We present some initial trials using optical vortices as a channel carrier or for signal modulation for a 1-km link. Plans for the next, 3-km test are also described
Chair(s): TBD
17:30 - Machine Learning-Based Channel Allocation for Secure Indoor Visible Light Communications
Rida Zia-ul-Mustafa, Hoa Le Minh and Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, CzechRepublic)
In this paper, a machine learning (ML)-based channel allocation algorithm is proposed to form a secure communication zone in indoor visible light communication (VLC) systems. The algorithm first employs the probabilistic neural network (PNN), which classifies the VLC transmitter (Tx) based on its proximity to the user's location. Subsequently, the selected Tx is used to establish a point-to-point channel allocation, hence forming a closed-access zone within a certain effective communication range. Through numerical simulations, it is observed that the single Tx-based VLC transmission confines the legitimate user in a pre-defined trust boundary for a secure transmission.
17:45 - Power Allocation for NOMA-Based Visible Light Communication Systems with DQN
Jia Wei Deng, Xuan Tang, Xian Wei, Pu Li and Jiaqi Li (East China Normal University, China); Xicong Li and Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
The spectral efficiency of the visible light communication system can be enhanced by using the non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) scheme. In this paper, we propose a deep Q network(DQN) framework-based power allocation scheme that maximizes the sum rate of a NOMA-based cellular VLC network with mobility support. The numerical results indicate that the optimisation process achieves improved performance in terms of sum data rate (SDR) by approximately 8.8, 7,and 4% compared with conventional algorithms, such as fixed power allocation, gain ratio power allocation, and genetic algorithms.
Chair(s): Prof. Adão Silva (Instituto de Telelcomunicações, Portugal)
17:00 - Impact of Reflections on Uplink Transmission in Optical Full Duplex Analog Radio Networks Using Centralized Sources
Marta Botella-Campos (Universitat Politècnica de València, Spain); Jan Bohata and Jan Vocílka (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Beatriz Ortega (ITEAM Research Institute, Spain); Jose Mora (Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Spain); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic)
In this paper, the impact of reflections in full duplex optical networks transmitting analog radio signal is investigated. The experimental testbed to reveal the impact has been proposed according to the verified pilot optical full duplex system based on a centralized optical source, which is used to transmit 5G new radio signal at the frequency band of 40 GHz. In the proposed testbed, a different level of reflected signal at the same wavelength is emulated for the range of relative reflected power (RRP) from 7 dB to 43 dB in intensity and phase modulation schemes. Signal reflections significantly degrade the uplink performance for RRPs below 30 dB for intensity modulation, whereas the phase modulation approach leads to a performance drop for RRP values below 40 dB.
17:10 - Optimizing Resource Allocation in 5G MIMO Networks Using DUDe Techniques
Konstantinos Tsachrelias, Chrysostomos Athanasios Katsigiannis and Vasileios Kokkinos (University of Patras, Greece); Apostolos Gkamas (University of Ioannina, Greece); Christos JBouras (University of Patras, Greece); Philippos Pouyioutas (University of Nicosia, Cyprus)
In the landscape of 5G networks, efficient resource allocation stands as a critical factor in meeting the diverse demands of applications and users. This paper delves into optimizing resource allocation within 5G Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) networks by leveraging Downlink/Uplink Decoupling (DUDe) techniques. MIMO technology, enabling the simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams, holds promise for boosting spectral efficiency. However, accommodating the dynamic and diverse user requirements poses a significant challenge in resource allocation. By employing advanced DUDe techniques, this research aims to dynamically allocate resources in 5G MIMO networks, seeking to enhance throughput, minimize latency, and optimize user satisfaction. Through simulation-based analysis, this paper highlights the efficacy of the proposed approach in significantly improving network performance and resource utilization.
17:20 - Enabling Spatial MIMO for Satellite Communications Without CSIT
Máximo Morales-Céspedes and Alejandro Lopez Barrios (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain)
Satellite Communications are proposed for supporting data traffic ubiquity at high data throughputs. Recent research works propose the use of MIMO precoding in multibeam satellitesor in spatial MIMO architectures where multiple satellites transmit pointing to the same region at the same frequency. However, their implementation is subject to discussion because of the need for channel state information at the transmitters, the cooperation among gateways and/or satellites or the correlation among channel responses in a purely Line-of-Sight (LoS) environment. In this work, we aim to describing the implementation of blind interference alignment (BIA) in satellite networks. Beyond the obvious benefits of the open-loop transmission, i.e., a return link is not required for providing channel state information at the transmitters (CSIT), BIA offers additional benefits in comparison with MIMO precoding for satellite communications such as the independence of the achievable rate on the channel responses of the users or the lack of cooperation for data sharing while achieving multiplexing gain. Simulation results show that BIA outperforms precoding schemes in the medium SNR range. These results motivate further research lines such as the use of BIA in low earth orbit satellite constellations of the impact of hardware impairments introduced by reconfigurable antennas.
17:30 - Enhancing Spectral Efficiency with Over-The-Air Multiuser-MIMO Enabled NOFS Signals
Tongyang Xu (Newcastle University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Yujian Ye and Tang Yi (Southeast University, China)
We innovate a novel over-the-air signal waveform termed non-orthogonal frequency shaping (NOFS), aiming for artificial intelligence air interface for future 6G communications. By reshaping sub-carriers using irregular Sinc (irSinc) patterns, the proposed NOFS waveform effectively reduces bandwidth and exhibits asymmetric shaping characteristics. The unique irSinc pattern empowers NOFS to utilize two-dimensional modulation schemes beyond the Mazo limit using simple detection techniques, where previously only maximum likelihood detection methods were possible. Moreover, NOFS demonstrates robustness in spectrally efficient communications even with high out-of-band power leakage. Additionally, the explainable nature of the neural network used in the NOFS waveform design provides insights into the signal patterns, enhancing transparency and trust in the system. Finally, an over-the-air signal transmission is operated in hardware validating the effectiveness and robustness of NOFS waveforms in real-world.
17:40 - Hybrid Equalization for mmWave Cell-Free Radio Stripes-Based Systems
Joumana Kassam (University of Aveiro & Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Daniel Castanheira (Instituto de Telecomunicações (IT) / University of Aveiro, Portugal); Adão Silva (Instituto de Telelcomunicações, Portugal); Rui Dinis (Universidade Nova de Lisboa & Nova IT, FCT-UNL, Portugal); Atílio Gameiro (Instituto de Telecomunicações / Universidade de Aveiro, Portugal)
Cell-free (CF) massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) stands out as a promising technology for 6G networks, offering distributed antennas over a geographical area rather than fixed base stations (BSs). Yet, the conventional CF network, with its star typologies, limits its practical implementation due to the high fronthaul and computational overhead. Consequently, integrating radio stripes (RS) with CF systems appears as a realistic and cost-effective approach to address these challenges, thereby enhancing system efficiency and scalability. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid analog-digital equalization algorithm, specifically designed for wideband millimeter wave (mmWave) CF mMIMO systems with RS deployment. To design the hybrid equalizer, the proposed algorithm uses only local channel information and the data estimate forwarded by the preceding AP. The APs analog equalizer is optimized based on the overall mean squared error (MSE) between the transmitted and received signals. Simulation results show that this sequential hybrid approach significantly reduces the signaling and information exchange demands.
17:50 - Active Intelligent Surfaces for Next Generation Radio Systems: An Overview on Large Intelligent Surfaces and Radio Stripes
Filipe João Conceição (Instituto de Telecomunicações & University of Coimbra, Portugal); Andreia Pereira (Instituto de Telecomunicações - University of Coimbra, Portugal); Marco A. C. Gomes (University of Coimbra, Portugal); Vitor Silva (Institute of Telecommunications, Portugal); Rui Dinis (Universidade Nova de Lisboa & Nova IT, FCT-UNL, Portugal)
Massive multiple-input-multiple-output (mMIMO) represents one of the most important breakthroughs in modern telecommunication theory. While actual smart antenna systems developed in the fifth generation (5G) era allow very large peak spectral efficiencies (SEs) in areas close to the base station, beyond-5G (B5G) systems will demand consistent, high SE over larger areas, so that the users can experience a ubiquitous service. For this purpose, the B5G mMIMO system's research tendency is based on the increase of antenna density in the communication structures. Following this approach, large intelligent surfaces (LIS) and radio stripes (RS) systems have been extensively studied in recent years. However, since LIS and RS systems take the mMIMO concept to an extreme level, it brings some important challenges to the table. Its practical implementation requires simplified hardware and signal processing techniques in order to maintain the entire system at an affordable complexity. This includes the development of efficient transmission/detection and resource allocation techniques. This work aims to explore the state-of-the-art designs of the LIS and RS systems while mentioning the upcoming communication challenges that will be present in future B5G wireless communication systems that incorporate an antenna ecosystem formed by several LIS and RS.
Chair(s): Dr. Andreas Johann Hörmer (Graz University of Technology, Austria)
17:00 - Fundamental Limitations Caused by Optical Propagation: Issues Relevant to Implement 'All-Optical' Technologies for Global Connectivity Using Space, Terrestrial and Underwater Communications
Arun Majumdar (San Diego Consulting, USA); Italo Toselli (Fraunhofer Institute of Optronics, System Technologies and Image Exploitation, Germany)
Designing optical transmission systems integrating satellites, HAPs, drones and underwater terminals require establishing global communication and connectivity. An examination of the effects of all possible propagation mechanisms is impossible in the context of a single paper. Therefore, only the fundamental limitations caused by optical propagation and potential solutions to handle these issues in various scenarios will be addressed in this conference contribution.
17:15 - Performance Evaluation and Comparison of VHF and S-Band Communication Links for the PRETTY Spacecraft
Andreas Johann Hörmer and Manuela Wenger (Graz University of Technology, Austria)
This paper conducts an evaluation of the communication links between the PRETTY spacecraft and its ground station, focusing on measuring the bandwidth efficiencies, and effective data rates of both the VHF and S-Band links. Through a detailed comparative analysis, the study explores the relative performance of the two frequency bands, considering the specific implications of utilising differing communication protocols. For the S-Band link, the paper compares the bandwidth efficiencies when operating with both Internet Protocol and CubeSat Space Protocol, assessing how each protocol method influences the effective data rate and bandwidth utilisation. Furthermore, by computing the real achieved performances based on the system design's inherent overheads - such as synchronization markers, frame headers, and packet headers - the study provides valuable insights into the operational efficiency of the spacecraft's communication system. The results presented offer a comprehensive analysis of the system's theoretical and actual performance, yielding key findings that are vital for future mission planning and optimization of data transmission strategies between CubeSat-class spacecraft and Earth-based receivers
17:30 - Bridging the Gap in Modulation Selection for Satellite Optical Communication
Andrea Petroni (Fondazione Ugo Bordoni, Italy); Ludovico Ferranti (Fondazione Ugo Bordoni, Italy & Sapienza University of Rome, Italy); Marcello Folli and Pierpaolo Salvo (Fondazione Ugo Bordoni, Italy)
The integration of space and terrestrial networks is envisaged as a promising approach to achieve enhanced quality of service in terms of coverage, throughput and data traffic management. To this end, optical wireless communication represents a suitable technology to realize reliable and high-rate ground-space and inter-satellite links. In this paper, we present an overview of all the components characterizing optical satellite link budget. Furthermore, we investigate the key relevance of link outage by jointly taking into account the effect of pointing loss and channel turbulence, representing random phenomena that can only be modeled statistically. Finally, communication feasibility is discussed for different ground-satellite configurations, showing how to select the most suited transmission scheme, i.e. modulation, so as to meet the requested reliability constraints and achieve the best performance.
17:45 - Converged Satellite to Fiber QKD Links: A Feasibility Analysis
Aristeidis Stathis (National Technical University of Athens & Institute of Communications & Computer Systems, Greece); Argiris Ntanos, Nikolaos Lyras, Giannis Giannoulis, Athanasios D. Panagopoulos and Hercules Avramopoulos (National Technical University of Athens, Greece)
This paper presents a comprehensive feasibility analysis designed to model Low Earth Orbit(LEO) satellite-to-ground communications for QKD, focusing on the 1550nm wavelength to facilitate the distribution of information through fiber segments. Discrete Variable Decoy State Polarization-based BB84 protocol is assumed whereas various detection setups and environmental conditions are simulated. Our analysis focuses on the receiver's design in terms of aperture and focal length to deliver a general framework by examining the coupling efficiency, a parameter strongly affecting the QKD satellite downlink. Through detailed simulation, we identify optimal configurations and operational parameters for various receiver designs, significantly enhancing the efficiency and reliability of satellite-to-ground QKD systems. The findings offer promising directions for extending the range of QKD systems, potentially revolutionizing secure communications by integrating satellite-transmitted quantum keys with terrestrial fiber networks. This study not only underscores the feasibility of advancing satellite-to-ground QKD technology but also lays the groundwork for future innovations in global quantum communications infrastructure.
Friday 19th July 2024
Chair(s): Prof. Beatriz Ortega (ITEAM Research Institute, Spain), Dr. Cristina Ponti (Roma Tre University, Italy)
09:00 - Tiny machine learning for resource-efficient networked embedded systems
Prof. E. Farella (Fondazione Bruno Kessler)
In the era of the Internet of Things (IoT), the deployment of resource-constrained embedded systems is proliferating, thus enabling the collection of heterogeneous data from objects, humans, animals and the environment. As the demand for intelligent decision-making at the edge grows, integrating machine learning and artificial intelligence into these networked embedded systems becomes imperative. However, the inherent limitations in terms of power, memory, and processing capabilities pose significant challenges. This talk explores the emerging paradigm of 'Tiny Machine Learning' (TinyML) as a transformative approach to enable intelligent processing on resource-constrained devices. We delve into the methodologies and techniques that make TinyML feasible for embedded systems and provide examples of complex AI tasks made 'tiny', emphasizing the need for efficient model architectures, lightweight algorithms, and favourable combinations of hardware and software.
Chair(s): Dr. Nuno M. Paulino (INESC TEC & Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Portugal)
10:00 - Anomalous Transmission from Finite-Size Metagratings for Wireless Communication Links
Cristina Ponti (Roma Tre University, Italy); Nikolaos L. Tsitsas (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece)
Metagratings designed for anomalous reflection and refraction are artificial structures that direct an imping radiation in directions that are not predicted by the Snell's law. Their properties allow manipulation of electromagnetic radiation, that can be exploited to improve coverage in wireless links through a layout which is easy to manufacture, and allows applications in different frequencies ranges, from millimeter waves to the optical regime. Metagratings are implemented as passive structures, through the periodic arrangement of a unit cell in which two dielectric materials having different permittivity are alternated. In this work, layouts for anomalous refraction are proposed, and analyzed as finite-length structures, for their practical use in communication scenarios.
10:15 - Multi-Layer Multi-Technology Firewall Optimisation in Beyond 5G Networks Using Machine Learning Classifiers
Jimena Andrade-Hoz (University of the West of Scotland, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Jose Maria Alcaraz Calero (University of the West of Scotland & School of Engineering and Computing, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Qi Wang (University of the West of Scotland, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Enhancing the security of Beyond 5G (B5G) and Pre-6G networks poses significant challenges, particularly in effectively implementing firewalls. Within a wide range of technologies aimed at implementing mitigation mechanisms, achieving optimal technology selection and rule set configuration within these diverse technologies is immensely complex. In addition, these rules are usually based on pre-configured template and lack of optimisation with information of real-time network status, often resulting in sub-optimal configurations. In this paper, an architecture that enables the optimisation of multi-layer multi-technology firewalls integrated in a B5G network testbed is presented. Our proposed framework supports network control monitoring and automatic deployment of firewall rules in three different virtual function implementations: iptables, Open vSwitch and Linux traffic control. After performing a comparison among four popular machine learning (ML) models for the optimal selection, our results show that RandomForest is the best algorithm for the proposed solution with a F1-score of 0.9083.
10:30 - Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Pattern Effect Compensation Using Digital Back-Propagation
Kyriakos Zoiros (Democritus University of Thrace, Greece); Zoe Rizou (University of Western Macedonia, Greece); Nikolaos Kanaropoulos (Democritus University of Thrace, Greece)
The feasibility of employing a digital backpropagation scheme to compensate for the pattern effects and their negative implications in a directly modulated reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA), due to the mismatch between the on-off keying data rate and the RSOA modulation bandwidth, is investigated and demonstrated through numerical simulations. The obtained results suggest that the impairment compensator (IC) can enhance a set of important characteristics of the encoded signal, as quantified by the improvement of key performance metrics. The IC can also relax the requirements for parameters that affect critically the RSOA pattern-dependence. The scheme is amenable to realization by application-specific photonic integrated circuits and hence can constitute a viable technological option for assisting the employment of RSOAs as intensity modulators.
10:45 - Energy Efficient Non-Orthogonal Signalling with Probabilistic Shaping for Wireless Transmissions
Xinyue Liu and Izzat Darwazeh (University College London, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
This work explores the realistic operation of a recently reported concept by the authors, which considers the use of probabilistic shaping for the non-orthogonal multicarrier spectrally efficient frequency division multiplexing (SEFDM) system. In this paper, we extend the operation of earlier signal and system designs, which considered only a simple AWGN channel, to realistic wireless environments with the focus of the studies on two frequency selective channels, namely a four-tap channel and Rummler's channel. The specialist system design for probabilistic shaping adopts a reverse concatenation architecture that cascades the constant composition distribution matching (CCDM) algorithm together with soft-decision forward error correction (SD-FEC) -LDPC code. The paper presents detailed modelling and simulation results, which clearly establish that, With pilot tone based channel estimation and equalisation, SEFDM with probabilistic shaping shows significant advantages, in both energy efficiency and robustness against wireless channel impairments, when compared to OFDM of the same spectral efficiency.
Chair(s): Prof. Luis Nero Alves (University of Aveiro, Portugal)
10:00 - 802.15.13 and 802.11bb: New standards for optical wireless communications
Prof. Volker Jungnickel
IEEE 802 has recently published two new standards for optical wireless communications. While IEEE Std 802.15.13-2023 is tailored for industrial, medical and backhaul applications, which require high reliability, low latency and zero jitter, IEEE Std 802.11bb-2023 is intended for the mass market aiming at low cost so that the reuse of existing silicon developed for 802.11, a.k.a. Wi-Fi has been defined. The talk will give a deeper insight into both standards, early product developments and open the discussion towards future work
Chair(s): Dr. Andrea Petroni (Fondazione Ugo Bordoni, Italy)
10:30 - Enhancing Underwater Visible Light Communication with End-To-End Learning Techniques
Jose Martin Luna-Rivera (Autonomous University of San Luis Potosi, Mexico); Jose Rabadan (ULPGC, Spain); Julio Rufo (Universidad de La Laguna, Spain); Victor Guerra (Pi Lighting, Switzerland); Carlos A. Gutiérrez (Universidad Autonoma de San Luis Potosi, Mexico); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (IDeTIC, Las Palmas University of Technology, Spain)
This paper investigates the potential of end-to-end learning as a means to enhance the performance and reliability of wireless communication systems. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on manual feature extraction and engineering-a process that is both time-consuming and requires specialized expertise-end-to-end learning promises to streamline the design of communication systems. It aims to reduce the complexity of signal processing algorithms, bolster system robustness against environmental conditions, and enable more efficient bandwidth utilization. Specifically, this study focuses on leveraging end-to-end learning to improve underwater visible light communication (VLC) systems. It facilitates the automatic learning of complex mappings between input signals and output symbols, eliminating the need for manually crafted features or prior channel knowledge. This method is anticipated to overcome challenges inherent in traditional signal processing techniques, such as sensitivity to channel variations and environmental disturbances, paving the way for the development of more efficient and resilient underwater communication systems. Importantly, the model's capability to be trained on large datasets is critical in underwater environments, where data availability is often scarce.
10:45 - Depth-Dependent Channel Characterization for Visible Light in Underwater Optical Wireless Links
Alessandro Ugolini and Federica Poli (University of Parma, Italy); Daniele Croce (University of Palermo, Italy); Stefano Mangione. (Università degli Studi di Palermo, Italy)
We describe depth-dependent effects that affect the propagation of light in underwater optical wireless links. We consider different wavelengths in the visible spectrum and compare them in terms of attenuation and losses as a function of depth. We show that some wavelengths are more suitable than others in this kind of applications.
11:00 - Relay-Aided Slotted Aloha for UAV-Assisted Mixed UOWC-RF Systems
Tijana Devaja and Srdjan Sobot (University of Novi Sad, Serbia); Milica Petkovic (Faculty of Technical Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Serbia); Marko Beko (ULHT/UNINOVA & UNINOVA, Caparica, Portugal); Dejan Vukobratovic (University of Novi Sad, Serbia)
In this paper, we design and analyse a relay-aided Slotted ALOHA solution for uplink random access in a mixed Underwater Optical Wireless Communications (UOWC)-Radio Frequency (RF)system. The first uplink phase represents the UOWC transmission between underwater devices and the floating buoys, which act as surface relays. The second uplink phase is performed by radio-frequency (RF) communications between buoys and an unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) hovering over the water surface. Analytical expression for end-to-end throughput is derived, and utilized to analyse performance dependence on the UOWC and RF channel conditions, as well as UAV position. The performance improvement due to employment of relaying is observed under various channel and traffic conditions.
11:15 - Application of Machine Learning to Signal Detection in Underwater Wireless Optical Communication Links
Mohamed Nennouche and Ali Khalighi (Ecole Centrale Méditerranée, France); Alexis Alfredo Dowhuszko (Aalto University, Finland); Djamal Merad and Jean-Marc Boi (Aix Marseille University, France)
We consider the application of machine-learning (ML) -based methods to signal demodulation for underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) links. The interest of this approach is when the underwater optical channel is subject to severe changes such as significant pointing errors, air bubbles, etc., requiring precise and agile channel estimation. The investigated ML method is based on the well-known K-nearest neighbors (KNN). We show the significant improvement of the link performance for different types of signaling schemes even under high data rates and low received optical powers. We also discuss the implementation aspects of the proposed approach, including its computational complexity.
Chair(s): Dr. Helder Fontes (INESC TEC and FEUP, Portugal)
10:00 - Optimal Design and Coverage for 5G Networks Operating in the mmWave Frequency Spectrum Using Mathematical Programming
Sergio Cordero (Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile); Pablo Adasme (University of Santiago de Chile, Chile); Hector Kaschel (Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile)
This paper presents two mathematical optimization models to solve problems related to the design and planning of 5G wireless communications networks using millimeter wave frequency spectrum. The first one allows for maximizing the number of covered users while minimizing the distances between each pair of base stations, and the distances required to connect each user to a unique base station. In this model, the number of base stations is fixed. The second model allows for optimizing the same objective function as the first one with an additional term used to minimize the total number of base stations required for the coverage. Notice that the problem to be addressed presents a high path loss. Consequently, the transmission distances should be reduced for different coverage transmission radii. Our models assume the existence of line-of-sight (LOS) for the links between the users and the base stations. Finally, we consider 10 instances with a maximum of 50 candidate location sites for the base stations and a maximum of 300 users for radial transmission distances of 150 and 200 meters. Our numerical results show that the proposed models can solve all the instances to optimality in a short CPU time effort.
10:15 - Improving Spectral and Power Efficiencies of a MISO-VLC System via Hybrid Multi-Objective Optimization
Wesley Costa (Hanze University of Applied Sciences, Brazil); Jair Adriano Lima Silva, Maria José Pontes and Marcelo E. Vieira Segatto (Federal University of Espirito Santo, Brazil); Helder Rocha (UFES, Brazil)
This study presents a methodology designed to optimize various parameters of each access point within a Multiple Input Single Output (MISO) Visible Light Communication (VLC) system. The primary objective is to enhance both power and spectral efficiencies. A MISO-VLC model is presented based on experimental evaluations and a problem formulation considering intermodulation distortions based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing modulation. A hybrid optimization approach is proposed, combining the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm III and the Multi-Objective Grey Wolf Optimizer. The proposed HMO's success was validated by a 66% reduction in transmitted power, maintaining the EVM performance metric seven at lower power transmission levels and minimizing the guard band to its lower bound.
10:30 - Neural Network-Based Stress Detection in Crop Multispectral Imagery for Precision Agriculture
Lídices Reyes-Hung (University of Santiago of Chile & Centre for Multidisciplinary Research in Telecommunication Technologies, Chile); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile); Arun Majumdar (San Diego Consulting, USA)
This study explores the application of object detection techniques using neural networks, specifically YOLOv7 and YOLOv8, to classify stress in potato crops using multispectral images obtained by drones. The results indicate that YOLOv8 excels in stress detection using RGBimages, while YOLOv7 shows higher accuracy with monochrome images, suggesting its suitability for specialized applications. The combination of RGB and monochromatic images significantly improved accuracy values for healthy and stressed plants, with figures of 0.917 and 0.914, respectively, and F1 score values of 0.902 for healthy plants and 0.881 for stressed plants. In addition, the importance of non-visible bands, such as NIR and RED EDGE, is highlighted to achieve complete and accurate evaluations. This work highlights the effectiveness of object detection techniques with neural networks in stress classification in agricultural images. It proposes future research to validate models in various crops and environmental conditions, thus improving precision agriculture practices.
10:45 - Artificial Intelligence in Home Hospitalization
Liliana Martínez (University of San Juan Argentina & Facultad de Ingeniería, Argentina); Florencia Carolina Reveco (USACH & CIMTT, Chile); Franco Guevara (Universidad Nacional de San Juan, Argentina); Cristina Laplagne (UNSJ, Argentina)
This study explores the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in home hospitalisation services in San Juan, Argentina. By analysing interdisciplinary team training and data collection methods, the research demonstrates how AI tools enhance patient care. A virtual survey among healthcare professionals highlights the benefits of 24-hour vital signs monitoring, revealing the impact of socio-cultural factors and treatment adjustments. The findings emphasize the transition from traditional data management to AI-driven applications, improving decision-making and patient outcomes.
Chair(s): Prof. Hoa Le Minh (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)), Prof. Wasiu O. Popoola (University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom (Great Britain)), Prof. Ioannis Tomkos (University of Patras, Greece)
12:00 - Techno-Economic and Feasibility Study of Point-To-Multipoint Communications in the Metro-Core
Polyzois Soumplis (National Technical University of Athens, Greece); Konstantinos Christodoulopoulos (University of Athens, Greece); Panagiotis Kokkinos (National Technical University of Athens & University of Peloponnese, Greece); Antonio Napoli and Mohammad Hosseini (Infinera, Germany); Marco Quagliotti (Telecom Italia, Italy); Emilio Riccardi (TelecomItalia Lab, Italy); Annachiara Pagano (Telecom Italia, Italy); Konstantinos Yiannopoulos (University of Peloponnese & Institute of Communication and Computer Systems, Greece); Emmanouel Varvarigos (National Technical University of Athens & Computer Technology Institute, Greece)
We investigate the introduction of point-to-multipoint (P2MP) transceivers in a realistic scenario inspired by a real metro-regional DWDM network. By establishing light-trees to aggregate traffic from multiple nodes towards the metro-core and backbone, we investigate how P2MP can complement existing point-to-point (P2P) architectures in reducing the number of required transceivers while optimizing the optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) budget. Our analysis of light-tree construction in relation to the available OSNR budget of the traffic aggregation nodes demonstrates that the efficient deployment of P2MP transceivers can significantly reduce reliance on P2P connections and lower overall transceiver costs, particularly when the OSNR issufficient to support light-tree lengths of approximately 120 km.
12:00 - Indoor Performance Simulation of Flexible OPV Cells Towards Visible Light Communication and Energy Harvesting
Daniel Ribeiro dos Santos (University of Limoges & XLIM Laboratory, France); Johann Bouclé (University of Limoges, France); Anne Julien-Vergonjanne (University of Limoges & XLIMCNRS 7252, France); Sadok Ben Dkhil and Marie Parmentier (Dracula Technologies, France); Pierre Combeau (Université de Poitiers, CNRS, XLIM, Poitiers, France); Stéphanie Sahuguède (XLIM UMR CNRS 7252 - University of Limoges, France)
Visible light communication (VLC) offers a solution to radiofrequency spectrum congestion by utilizing indoor lighting for illumination and communication purposes. Recent research explores the use of photovoltaic devices as receivers for simultaneous data detection and energy harvesting, representing an important advancement towards sustainable IoT nodes. Furthermore, emerging solar cells such as organic photovoltaics (OPVs) exhibit properties that meet the requirements of IoT, especially due to their large flexibility. However, it is crucial to validate flexible photovoltaic receivers performance in complex indoor environments while considering diffuse light pathway. In this context, we introduce the first ever curved OPV model, employing Monte Carlo ray tracing for simulation of light reception, associated to experimental validation. The new model allows the estimation of the channel impulse responses in realistic indoorsettings, highlighting the efficacy of curved OPV devices in typical VLC scenarios for IoT.
12:00 - Impact of the CMOS Pixel Clock on Optical Camera Communication Using Rolling Shutter Mode
Raul Zamorano-Illanes, Zabih Ghassemlooy, Othman Isam Younus and Xicong Li (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Stanislav Zvanovec (Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile); Sebastian Gutierrez (Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad Autonoma de Chile, Santiago, Chile)
This study delves into the impact of the pixel clock on the frequency response of Optical Camera Communication (OCC) systems utilizing rolling shutter mode. Employing an experimental approach, we examine how variations in the clock influence the frequency response of a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor within OCC links. Our setup incorporates an algorithmic methodology to manipulate and assess internal camera parameters, focusing on the minimum exposure times to optimize signal capture and processing. The findings reveal a direct relation between the clock and the achievable frame rate. It is a first approach to delineating its effect on the temporal resolution and bandwidth of the communication channel, showing the importance of these insights for enhancing the design and efficiency of OCC systems. Our research contributes to understand the hardware limitations and opens future explorations into maximizing the communication performance.
12:00 - A Deep Space Challenge for Future Human Communications: Achieving Mars Through Light
Mauro Biagi (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy)
With the growing investments and projects toward human landing on Mars, allowing fast and reliable communication from Earth-to-Mars and viceversa is a real need. In this regard, in the past, radio communications have been always utilized while it is known that optical signals can deliver information at higher speed. Some drawbacks in the communications must be still overcome as well as, for example, the Sun position that is a huge obstacle from the propagation point of view and also a source of interference. In this contribution the strength points and weaknesses of different architectures are considered so as to highlight the steps still to be run to achieve reliable and fast communication between Earth and Mars. The future key for enabling continuous communication may be the use of non-Keplerian orbits by satellite relay(s) that allows to avoid communication discontinuities in case of Earth-Mars conjunction.
12:00 - Video Steganography System Based on Optical Flow for Object Detection
Abdellatif Zouak, Krishna Busawon and Xicong Li (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain))
Steganography is the art of covert communication; the secret message is hidden in a coverless file. Steganography and steganalysis systems become more important in many areas of information security. In contrast with cryptography, it is the existence of the secret message that is hidden and not its meaning. In this paper, a video steganography method is proposed to embed and extract the hidden data based on the motion estimation of optical flow. The proposed method is based on the selection of macroblocks with the highest optical flow magnitude. The potential of this method is to produce a minimum distortion in the stego video as it is evaluated using multiple factors of the imperceptibility of a successful video steganography, the proposed system has been tested and evaluated in 8 videos sized of 240x352, where the results illustrate the efficacity of the proposed modelling scheme.
12:00 - Research on Vehicle-To-Vehicle 2xn MIMO-VLC System Based on an Improved Genetic Algorithm
Rongrong Yin, Mingqi He, Xingyue Shen, Hao Qin, Shaoying Ma and Chun Lang (Yanshan University, China)
This paper proposes a vehicle-to-vehicle 2xn MIMO-VLC system model based on an improved genetic algorithm to achieve the purpose of improving the bit error rate (BER) performance of vehicle-to-vehicle visible light commutations systems in the presence of interfering vehicles. The model uses two headlights of the car as transmitters and n photoelectric detectors (PD) as receivers. In the presence of interfering vehicles, the improved genetic algorithm was used to optimize the light sensitive area parameters and the half angle of field of view parameters of the nPDs, and then the signal-to-noise ratios received by the n PDs with optimized structural parameters were processed using the maximum ratio merging method to finalize the data reception. The results of the study show that the vehicle-to-vehicle 2xn MIMO-VLC system model using improved genetic algorithm to optimize the PD structural parameters has a positive effect in reducing the system BER and the degree of BER fluctuation.
12:00 - On Using the Raspberry Pi Camera to Receive 8-PAM Signals in Optical Camera Communication
Miguel Rêgo (University of Aveiro & Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Vicente Matus (IDeTIC-ULPGC, Spain); Othman Isam Younus (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Alexis Alfredo Dowhuszko (Aalto University, Finland); Zabih Ghassemlooy (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); Monica Figueiredo (Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Portugal); Pedro Fonseca (University of Aveiro & Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal); Luis Nero Alves (DETI, Universidade of Aveiro, Instituto de Telecomunicações, Portugal)
Optical Camera Communication (OCC) has emerged as a way of implementing Optical Wireless Communication (OWC) without the need of adding an additional interface to smart devices equipped with cameras, and is suitable for applications in Internet of Things (IoT), secure communications, indoor positioning and electromagnetic interference sensitive scenarios. Given the fact that a camera consists of an array of photodetectors connected to analog-to-digital converters, we can leverage this fact to implement not only binary signal reception, but also a multi-level Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) receiver. In this paper, we explore the usage of the Raspberry Pi Camera V2.1 as a receiver for implementing 8-PAM OCC, focusing on the technical characteristics of this camera and identifying the limitations that arise from its low cost. A decoder algorithm is proposed, aimed at circumventing the identified limitations with signal processing solutions. The proposed algorithm was experimentally validated in an indoor scenario and a Symbol Error Rate (SER) was measured for up to 1.8m, remaining under 1.3%.
12:00 - Performance Analysis of a VLC System Applied to a Hospital Environment for IoT-Based Smart Patient Monitoring
Benjamin Fernández Vizcarra and Pablo Palacios Játiva, Dr. (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile); Cesar Azurdia (Universidad de Chile, Chile); Nicolás Boettcher (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile); David Zabala-Blanco (Universidad Catolica del Maule, Chile); Miguel Gutierrez Gaitan (PUC (Chile), Chile & CISTER (Portugal), Portugal); Ismael Soto (University of Santiago, Chile)
This article discusses the deployment of effective communication networks for smart IoT-based smart patient monitoring in medical facilities, advocating for the adoption of Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology. Initially, the physical scenario is analyzed, taking into account factors such as line-of-sight (LOS) and non line-of-sight (NLOS) channel components. Furthermore, a transmitter is designed to offer a substitute in the event of potential disruptions due to patient motion or loss of line-of-sight elements. The performance of the proposed system is verified under certain performance metrics, such as the Channel Impulse Response (CIR) and the Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF), with respect to power measurements at different points. The results highlight the effects that NLOS rays have on the received data and the received power. Therefore, this study serves as a step towards the development of more sophisticated systems for patient monitoring using enabling technologies such as VLC.
12:00 - Multichannel Wiener-Like Filter and Multinomial Karhunen–Loève Transform for Estimation of Distributed Signals
Phil G Howlett and Anatoli Torokhti (University of South Australia, Australia); Pablo Soto-Quiros (The Costa Rica Institute of Technology, Costa Rica)
We address the problem of distributed signal processing where a source random signal is observed by local sensors and then transmitted to a fusion-reconstruction center (FRC) for the signal estimation. An optimal determination of the sensors and the FRC requires extensions of the Wiener filter and Karhunen–Loève transform. In this paper, the associated extensions are provided. Unlike the recent techniques in [3, 14], the proposed method allows us to avoid the bottlenecks associated with an accumulation of the errors and an additional computational work. This leads to a faster performance of the distributed random signal estimation.
12:00 - Experimental Evaluation of Wearable LED Strip for Outdoor Optical Camera Communications Systems
Eleni Niarchou (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain); Vicente Matus (IDeTIC-ULPGC, Spain); Rafael Perez-Jimenez (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain); Jose Rabadan (IDeTIC-ULPGC, Spain); Victor Guerra (Pi Lighting, Switzerland)
In this paper, we experimentally demonstrate an outdoor optical camera communications (OCC) system utilizing a wearable light-emitting diode (LED) as the transmitter. Explore the practicality of employing commercial devices, such as an LED strip and a smartphone, in OCC links for simultaneous monitoring and communication purposes. In particular, a strip of red-green-blue (RGB) LEDs is modulated to transmit data for user identification via visible light. Each color (red, green, blue and yellow) serves as an indicator of the user's status. Our system exhibits potential applications in high-risk environments where monitoring the physical well-being of individuals is crucial.
12:00 - Small Range Site Diversity Considerations Based on Long-Term Data from a Very Dense Rain Gauge Network
Franz Teschl and Reinhard Teschl (Graz University of Technology, Austria)
Site diversity is a technique used to improve the reliability of satellite communication systems particularly during severe rain events. The technique works by linking two or more ground stations that receive the same signal and by compensating deep rain fades that occur in one station by another station where the signal is better at the time. In order to find ideal distances between the ground stations, the spatial correlation of rainfall is investigated based on long-term data from a very dense rain gauge network in the Alpine foreland of southeast Austria in the region of Feldbach. The data reveals that the correlation coefficient between the rain rate time series of two rain gauges drops below 0.5 if the instruments are more than 4 km away. A local minimum for the correlation, and thus, an appropriate separation between two ground stations occurs at distances around 13 km.
12:00 - Comparison of Swarm Intelligence Methods for Joint Resource Orchestration in Open Radio Access Network
Dimitrios Pliatsios (University of Western Macedonia, Greece)
The radio access network (RAN) will be an integral part of the sixth generation (6G) of mobile networks. By using several advanced technologies (e.g., virtualization, cloud, and edge computing), it aims to address the stringent networking and computing requirements of new applications and offer high quality of service and experience levels to the consumers. However,the optimal allocation of computing and radio resources can be challenging due to the heterogeneity of the network and the stringent constraints imposed by the new application requirements. This work is focused on leveraging swarm intelligence methods in an Open RAN to offer a zero-touch management network architecture that autonomously orchestrates its resources taking into account several constraints. Specifically, three swarm intelligence methods are evaluated and compared, namely the Grey Wolf Optimizer, the Salp Swarm Algorithm, and the Particle Swarm Optimization. The results show that the Grey Wolf Optimizer features the best performance in solving the joint offloading and resource allocation problem in edge computing scenarios.
12:00 - Leveraging a Digital Chirp Spread Spectrum Detector for LPWAN Wake-Up Receivers
Pol Maistriaux (Uclouvain, Belgium); Marco Gonzalez (ICTEAM, Belgium); Jerome Louveaux (Université Catholique de Louvain, Belgium); David Bol (Université Catholique de Louvain, Belgium)
Wireless sensor networks are emerging as serious candidates to detect critical events in ecosystems and remote areas. To maximize their coverage in those environments, mesh networkscan be used. However, they require more complex medium access control, at the cost of higher power consumption for the sensor-node RF receiver. The alternative paradigm of wake-up receivers (WuRXs) offers a possible solution to this issue. The objective is to offer an ultra-low-power detection mode to wake up the main receiver, placed in deep sleep, only when an incoming RF signal is found. Previous WuRXs designed for short-range communications fail to reach the sensitivity level required for longer distances, partly due to their simple digital baseband (DBB) processor. In this work, we investigate the use of chirp spread spectrum (CSS), already well-known thanks to LoRa, as an efficient modulation scheme for long-range WuRXs, leveraging its high processing gain and acceptable complexity. To validate this approach, we propose a digital hardware implementation and provide synthesis results in 65-nm CMOS. Compared to state-of-the-art long-range WuRXs, the proposed DSP improves the sensitivity by 11.8 dB with a limited 23% power consumption overhead.
12:00 - Development of a Cognitive IoT-Enabled Smart Campus
Imanol Picallo and Hicham Klaina (Universidad Publica de Navarra, Spain); Peio Lopez Iturri (Universidad Publica de Navarra, Spain); Leyre Azpilicueta and Mikel Celaya-Echarri (Public University of Navarre, Spain); Jose Javier Astrain, Jesus Villadangos and Francisco Falcone (Universidad Publica de Navarra, Spain)
The evolution from Smart to Cognitive Cities takes advantage, among others, of advanced communication technologies in order to increase interactivity levels. In this work, an analysis of wireless connectivity within the framework of a Smart Campus pilot at the Public University of Navarra in Spain is presented. By means of in-house implemented hybrid deterministic code, multiple wireless connectivity conditions with different operating frequencies are presented. The use of these tools provides accurate coverage/capacity analysis of large, complex scenarios, aiding in the design of network devices as well as overall network topology in order to optimize overall performance.
12:00 - Enabling Self-Powered Analog Voice Communication with Photovoltaic Cells and Optical Wireless Links Communication
Mircea Hulea (Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi, Romania); Othman Isam Younus (Northumbria University, United Kingdom (Great Britain)); George-Iulian Uleru and Alexandru Barleanu (Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, Romania)
The growing demand for energy-efficient communication systems has triggered the interest in using photovoltaic (PV) panels to power optical receivers in Visible Light Communication (VLC) systems. While this approach offers the enticing advantage of self-powered operation, it comes with a significant drawback of a limited bandwidth. This limitation severely restricts the maximum data rate achievable through VLC channels, especially when compared to digital audio transmission which requires a high bandwidth due to sampling and resolution needs. Therefore, a key challenge lies in finding a balance between the energy-harvesting benefits of PV receivers and the need for sufficient data rate for specific VLC applications. This work evaluates experimentally the possibility to transmit using VLC the voice in analogue domain when the transmission of the digital conversion of this signal is not possible due to limited bandwidth of the PV-based receiver. The results show that speech can be received properly in analogue domain when the transmission of the digital conversion is not possible due to limited bandwidth of the PV panel.
12:00 - Estimation of Number of Sources Impinging on A Uniformly Spaced Linear Array of Sensors
Gaetano Scarano (Università La Sapienza di Roma, Italy); Stefania Colonnese (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy); Roberto Cusani (Università La Sapienza di Roma, Italy); Mauro Biagi (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy)
A novel estimation method of number of sources emitting waves on an uniformly spaced linear array of sensors is described. Similarly to well-known existing techniques, it is inspired by certain properties hold by the eigenvalues of the correlation matrix of the received signal. Numerical results show the feasibility of the here presented novel estimator in comparison with popular, Information Theoretic Criteria based estimators.
Click here to download the pdf version of the detailed program
Page updated on: 23 Jul 2024 - 9:58
Technical Cosponsors
Financial Sponsors
Important dates
Today isFriday, 28 November 2025
Full paper due14 March 2024 Expired
Notification of acceptance23 April 2024 Expired
Final paper submission31 May 2024 Expired
Registration opens1 April 2024 Closed
Early bird registration closes31 May 2024 Closed
Supporting grants application deadlineClosed
© CSNDSP 2024
Developed by Uniroma3
Developed by Uniroma3











